Genome-wide comparative analysis of CC1 Staphylococcus aureus between colonization and infection
- PMID: 39343893
- PMCID: PMC11441255
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-024-02076-z
Genome-wide comparative analysis of CC1 Staphylococcus aureus between colonization and infection
Abstract
Background: Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most important bacteria in human colonization and infection. Clonal complex1 (CC1) is one of the largest and most important S. aureus CCs, and it is a predominant clone in S. aureus colonization and can cause a series of S. aureus infections including bloodstream infections. No studies on the relationship of CC1 S. aureus between colonization and infection have been published.
Methods: To figure out if there are some significant factors in CC1 S. aureus help its colonization or infection, 15 CC1 S. aureus isolates including ten from colonization and five from bloodstream infections were enrolled in this study. Whole-genome sequencing and bioinformatics analysis were performed.
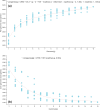
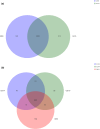
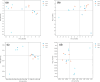
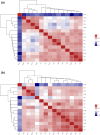
Results: Virulence factor regulators XdrA, YSIRK signal peptide, CPBP family and OmpR family specifically found in infection isolates can promote virulence factors and enhance the pathogenicity of S. aureus. In addition, some significant differences in metabolism and human diseases were discovered between colonization and infection. Fst family of type I toxin-antitoxin system that mainly maintains stable inheritance was specifically found in CC1 S. aureus colonization isolates and might help S. aureus survive for colonization. No significant differences in genomic evolutionary relationship were found among CC1 S. aureus isolates between colonization and infection.
Conclusions: Virulence factor regulators and metabolic state can promote CC1 S. aureus pathogenic process compared with colonization, and it seems that the strains of colonization origin cannot have pathogenic potential. Experimental confirmation and a bigger number of CC1 S. aureus strains are necessary for further study about the details and mechanism between colonization and infection.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; CC1; Colonization; Genome; Infection.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genomic characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from patients admitted to intensive care units of a tertiary care hospital: epidemiological risk of nasal carriage of virulent clone during admission.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jun 4;12(6):e0295023. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02950-23. Epub 2024 May 6. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38709078 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic analysis of Staphylococcus aureus from the West African Dwarf (WAD) goat in Nigeria.Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2021 Aug 19;10(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s13756-021-00987-8. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2021. PMID: 34412702 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characteristics and risk factor analysis of Staphylococcus aureus colonization put insight into CC1 colonization in three nursing homes in Shanghai.PLoS One. 2021 Oct 7;16(10):e0253858. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253858. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34618818 Free PMC article.
-
Population genetics and the evolution of virulence in Staphylococcus aureus.Infect Genet Evol. 2014 Jan;21:554-62. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2013.04.026. Epub 2013 Apr 27. Infect Genet Evol. 2014. PMID: 23628638 Review.
-
Co-evolutionary aspects of human colonisation and infection by Staphylococcus aureus.Infect Genet Evol. 2009 Jan;9(1):32-47. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2008.09.012. Epub 2008 Oct 19. Infect Genet Evol. 2009. PMID: 19000784 Review.
Cited by
-
Overlapping and specific bacterial communities in the gut and reproductive system of Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) (Diptera: Tephritidae) adults.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jun 2;16:1567154. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1567154. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40529586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dryden MS. Skin and soft tissue infection: microbiology and epidemiology. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2009;34(Suppl 1):S2-7. 10.1016/s0924-8579(09)70541-2. - PubMed
-
- Cardona AF, Wilson SE. Skin and soft-tissue infections: a critical review and the role of telavancin in their treatment. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;61(Suppl 2):S69-78. 10.1093/cid/civ528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

