RNA silencing is a key regulatory mechanism in the biocontrol fungus Clonostachys rosea-wheat interactions
- PMID: 39343898
- PMCID: PMC11441109
- DOI: 10.1186/s12915-024-02014-9
RNA silencing is a key regulatory mechanism in the biocontrol fungus Clonostachys rosea-wheat interactions
Abstract
Background: Small RNA (sRNAs)- mediated RNA silencing is emerging as a key player in host-microbe interactions. However, its role in fungus-plant interactions relevant to biocontrol of plant diseases is yet to be explored. This study aimed to investigate Dicer (DCL)-mediated endogenous and cross-kingdom gene expression regulation in the biocontrol fungus Clonostachys rosea and wheat roots during interactions.
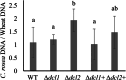
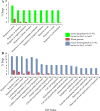
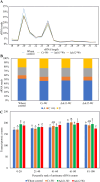
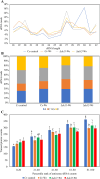
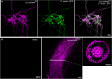
Results: C. rosea Δdcl2 strain exhibited significantly higher root colonization than the WT, whereas no significant differences were observed for Δdcl1 strains. Dual RNA-seq revealed the upregulation of CAZymes, membrane transporters, and effector coding genes in C. rosea, whereas wheat roots responded with the upregulation of stress-related genes and the downregulation of growth-related genes. The expression of many of these genes was downregulated in wheat during the interaction with DCL deletion strains, underscoring the influence of fungal DCL genes on wheat defense response. sRNA sequencing identified 18 wheat miRNAs responsive to C. rosea, and three were predicted to target the C. rosea polyketide synthase gene pks29. Two of these miRNAs (mir_17532_x1 and mir_12061_x13) were observed to enter C. rosea from wheat roots with fluorescence analyses and to downregulate the expression of pks29, showing plausible cross-kingdom RNA silencing of the C. rosea gene by wheat miRNAs.
Conclusions: We provide insights into the mechanisms underlying the interaction between biocontrol fungi and plant roots. Moreover, the study sheds light on the role of sRNA-mediated gene expression regulation in C. rosea-wheat interactions and provides preliminary evidence of cross-kingdom RNA silencing between plants and biocontrol fungi.
Keywords: Triticum aestivum; Beneficial fungi; Cross-kingdom RNA silencing; DCL; Defense induction; Gene silencing; Growth promotion; RNA interference; miRNA; sRNAs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Piombo E, Vetukuri RR, Tzelepis G, Jensen DF, Karlsson M, Dubey M. Small RNAs: a new paradigm in fungal-fungal interactions used for biocontrol. Fungal Biol Rev. 2024;48:100356. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

