BEEAF2 Score: A New Risk Stratification Score for Patients With Stage B Heart Failure From the KUNIUMI Registry Chronic Cohort
- PMID: 39344672
- PMCID: PMC11681443
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.124.034793
BEEAF2 Score: A New Risk Stratification Score for Patients With Stage B Heart Failure From the KUNIUMI Registry Chronic Cohort
Abstract
Background: Stage B heart failure (HF) refers to structural heart disease without signs or symptoms of HF, so that early intervention may delay or prevent the onset of overt HF. However, stage B HF is a very broad concept, and risk stratification of such patients can be challenging.
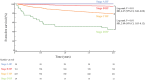
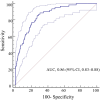
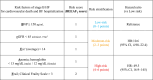
Methods and results: We conducted a prospective study of data for 1646 consecutive patients with HF from the KUNIUMI (Kobe University Heart Failure Registry in Awaji Medical Center) registry chronic cohort. The definition of HF stages was based on current guidelines for classification of 29 patients as stage A HF, 761 as stage B HF, 827 as stage C HF, and 29 patients as stage D HF. The primary end point was the time-to-first-event defined as cardiovascular death or HF hospitalization within 2.0 years of follow-up. A maximum of 6 adjustment factor points was assigned based on Cox proportional hazards analysis findings for the hazard ratio (HR) of independent risk factors for the primary end point: 1 point for anemia, estimated glomerular filtration rate <45 mL/min per 1.73 m2, brain natriuretic peptide ≥150 pg/mL, and average ratio of early transmitral flow velocity to early diastolic mitral annular velocity >14, and 2 points for clinical frailty scale >3. Patients with stage B HF were stratified into 3 groups, low risk (0-1 points), moderate risk (2-3 points), and high risk (4-6 points). Based on this scoring system (BEEAF2 [brain natriuretic peptide, estimated glomerular filtration rate, ratio of early transmitral flow velocity to early diastolic mitral annular velocity, anemia, and frailty]), the outcome was found to become worse in accordance with risk level. High-risk patients with stage B HF and patients with stage C HF showed similar outcomes.
Conclusions: Our scoring system offers an easy-to-use evaluation of risk stratification for patients with stage B HF.
Keywords: echocardiography; preclinical heart failure; risk stratification; stage B heart failure.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Plasma N-terminal protype-B natriuretic peptide and restrictive mitral flow to risk-stratify patients with stage B heart failure.Clin Cardiol. 2009 Dec;32(12):711-7. doi: 10.1002/clc.20617. Clin Cardiol. 2009. PMID: 20027664 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Significance of Get With the Guidelines-Heart Failure Risk Score in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure After Hospitalization.J Am Heart Assoc. 2018 Sep 4;7(17):e008316. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.008316. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018. PMID: 30371158 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the Get With The Guideline-Heart Failure risk score in Japanese patients and the potential improvement of its discrimination ability by the inclusion of B-type natriuretic peptide level.Am Heart J. 2016 Jan;171(1):33-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2015.10.008. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Am Heart J. 2016. PMID: 26699598
-
Optimal noninvasive assessment of diastolic heart failure in patients with atrial fibrillation: comparison of tissue doppler echocardiography, left atrium size, and brain natriuretic peptide.J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2008 Jun;21(6):689-96. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2007.08.014. Epub 2007 Sep 29. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2008. PMID: 17904810
-
Toward a Universal Definition of Etiologies in Heart Failure: Categorizing Causes and Advancing Registry Science.Circ Heart Fail. 2024 Apr;17(4):e011095. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.123.011095. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Circ Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 38626067 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM, Deswal A, Drazner MH, Dunlay SM, Evers LR, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation. 2022;145:e895–e1032. doi: 10.1161/cir.0000000000001063 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ammar KA, Jacobsen SJ, Mahoney DW, Kors JA, Redfield MM, Burnett JC Jr, Rodeheffer RJ. Prevalence and prognostic significance of heart failure stages: application of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Heart Failure Staging Criteria in the community. Circulation. 2007;115:1563–1570. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.106.666818 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM, Deswal A, Drazner MH, Dunlay SM, Evers LR, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation. 2022;145:e876–e894. doi: 10.1161/cir.0000000000001062 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor‐Avi V, Afilalo J, Armstrong A, Ernande L, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Goldstein SA, Kuznetsova T, et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2015;28:1–39.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2014.10.003 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

