Immunofluorescent detection of protein CoAlation in mammalian cells under oxidative stress
- PMID: 39344817
- PMCID: PMC11463958
- DOI: 10.1242/bio.061685
Immunofluorescent detection of protein CoAlation in mammalian cells under oxidative stress
Abstract
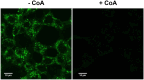
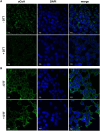
Previously, we reported the generation and characterisation of highly specific anti-CoA monoclonal antibodies capable of recognizing CoA in various immunological assays. Utilizing these antibodies in conjunction with mass spectrometry, we identified a wide array of cellular proteins modified by CoA in bacteria and mammalian cells. Furthermore, our findings demonstrated that such modifications could be induced by oxidative or metabolic stress. This study advances the utility of anti-CoA monoclonal antibodies in analysing protein CoAlation, highlighting their effectiveness in immunofluorescent assay. Our data corroborates a significant increase in cellular protein CoAlation induced by oxidative agents. Additionally, we observed that hydrogen-peroxide induced protein CoAlation is predominantly associated with mitochondrial proteins.
Keywords: Anti-CoA mabs; Cell signalling; Coenzyme A; Immunofluorescent analysis; Oxidative stress; Protein CoAlation.
© 2024. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests No competing interests declared.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Coenzyme A and protein CoAlation levels are regulated in response to oxidative stress and during morphogenesis in Dictyostelium discoideum.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 Apr 2;511(2):294-299. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.02.031. Epub 2019 Feb 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019. PMID: 30797553 Free PMC article.
-
Extensive Anti-CoA Immunostaining in Alzheimer's Disease and Covalent Modification of Tau by a Key Cellular Metabolite Coenzyme A.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Oct 15;15:739425. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.739425. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34720880 Free PMC article.
-
Protein CoAlation: a redox-regulated protein modification by coenzyme A in mammalian cells.Biochem J. 2017 Jul 11;474(14):2489-2508. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170129. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 28341808 Free PMC article.
-
Coenzyme A, protein CoAlation and redox regulation in mammalian cells.Biochem Soc Trans. 2018 Jun 19;46(3):721-728. doi: 10.1042/BST20170506. Epub 2018 May 25. Biochem Soc Trans. 2018. PMID: 29802218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coenzyme A levels influence protein acetylation, CoAlation and 4'-phosphopantetheinylation: Expanding the impact of a metabolic nexus molecule.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2021 Apr;1868(4):118965. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2021.118965. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2021. PMID: 33450307 Review.
References
-
- Baković, J., Yu, B. Y. K., Silva, D., Chew, S. P., Kim, S., Ahn, S.-H., Palmer, L., Aloum, L., Stanzani, G., Malanchuk, O.et al. (2019). A key metabolic integrator, coenzyme A, modulates the activity of peroxiredoxin 5 via covalent modification. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 461, 91-102. 10.1007/s11010-019-03593-w - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baković, J., Yu, B. Y. K., Silva, D., Baczynska, M., Peak-Chew, S. Y., Switzer, A., Burchell, L., Wigneshweraraj, S., Vandanashree, M., Gopal, B.et al. (2021). Redox regulation of the quorum-sensing transcription factor AgrA by Coenzyme A. Antioxidants 10, 841. 10.3390/antiox10060841 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dusi, S., Valletta, L., Haack, T. B., Tsuchiya, Y., Venco, P., Pasqualato, S., Goffrini, P., Tigano, M., Demchenko, N., Wieland, T.et al. (2014). Exome sequence reveals mutations in CoA synthase as a cause of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 94, 11-22. 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.11.008 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

