Relationship between SGLT2 inhibitor use and specific cancer types: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39344829
- PMCID: PMC11444652
- DOI: 10.1080/20565623.2024.2400797
Relationship between SGLT2 inhibitor use and specific cancer types: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
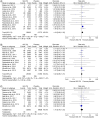
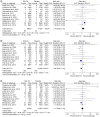
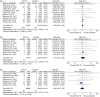
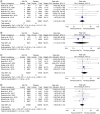
Aim: The study aimed to explore the incidence of cancer as an adverse event to SGLT2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) use in Type 2 diabetes.Materials & methods: The study followed PRISMA guidelines to pool RCTs conforming the inclusion criteria. Random effects model was used to pool risk ratios.Results & conclusion: After reviewing 19 studies, the analysis suggested a possible increased risk of reproductive, breast, thyroid, hematologic/lymphatic, urinary, skin and skeletal cancers with SGLT2i use. Conversely, lower incidences of respiratory and cardiovascular cancers were noted. However, these associations lacked statistical significance. Caution is advised in using SGLT2i due to potential cancer risks, especially in diabetic patients prone to cancer. More RCTs are essential due to limited research in this area.
Keywords: SGLT2 inhibitors; antidiabetic medication; cancer incidence; cancer risk; diabetes mellitus; malignancy; meta-analysis; organ specific cancers; sodium-glucose transport protein 2 inhibitors; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Plain language summary
SGLT2 inhibitors, widely used to manage Type 2 diabetes, provide benefits for blood sugar control, cardiovascular health and kidney function. However, their impact on cancer risk remains unclear. This review and meta-analysis examined randomized controlled trials to evaluate cancer outcomes in adults using SGLT2 inhibitors. Findings indicated mixed effects on various cancer types, with some inhibitors potentially increasing risk while others showed no significant impact. Further research is essential to clarify the relationship between SGLT2 inhibitors and cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Brown E, Heerspink HJL, Cuthbertson DJ, Wilding JPH. SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists: established and emerging indications. Lancet. 2021;398(10296):262–276. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0140673621005365 - PubMed
-
- Gilbert MP. Screening and treatment by the primary care provider of common diabetes complications. Med Clin North Am. 2015;99(1):201–219. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0025712514001503 - PubMed
-
- Tseng C-H. Metformin is associated with a lower risk of colorectal cancer in Taiwanese patients with Type 2 diabetes: a retrospective cohort analysis. Diabetes Metab. 2017;43(5):438–445. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28438547 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
