Effects of Ward Noise Management on Mental Health and Hip Function in Elderly Patients Undergoing Total Hip Arthroplasty
- PMID: 39345087
- PMCID: PMC11539983
- DOI: 10.4103/nah.nah_87_24
Effects of Ward Noise Management on Mental Health and Hip Function in Elderly Patients Undergoing Total Hip Arthroplasty
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to explore the influence of ward noise management on the mental health and hip joint function of elderly patients post-total hip arthroplasty.
Methods: The retrospective analysis involved the medical records of 160 elderly patients who underwent total hip arthroplasty at Nanchang First Hospital from March 2021 to January 2023. The observation group received ward noise management (n = 75) and the control group received perioperative routine management (n = 85). The noise level, Self-rating Depression Scale (SDS), Self-rating Anxiety Scale (SAS), the Generic Quality of Life Inventory-74 (GQOLI-74), Harris Hip Score (HHS) system, and satisfaction scale were used to evaluate patients. T test and chi-square tests were used for statistical analysis.
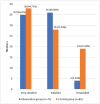
Results: The observation group exhibited a significantly lower noise level compared to the control group (P < 0.05). No significant differences were observed in the general information and preoperative SDS, SAS, HHS, and GQOLI-74 scores between the two groups (P > 0.05). No significant differences were observed in the SDS and HHS between the two groups 7 days after the operation (P > 0.05). The observation group presented a significantly lower SAS score than the control group 7 days after the operation (P < 0.05). The score of the observation group 7 days after the operation was lower than that before the operation (P < 0.05). At 7 days after the operation, the observation group showed a higher score in the "social function" dimension of GQOLI-74 compared to the control group (P < 0.05), and the satisfaction of the observation group was significantly higher than that of the control group (94.67 vs. 77.65%, P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Ward noise management can help reduce anxiety among elderly patients after total hip arthroplasty, improve their quality of life and social function, and obtain higher satisfaction.
Copyright © 2024 Noise & Health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Similar articles
-
Impact of precision nursing intervention based on DCO model on joint function and quality of life of elderly hip arthroplasty patients.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Apr 28;20(1):421. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05820-1. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40296148 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Rehabilitation Nursing under the Guidance of the Health Action Process Approach Model on Perioperative Nursing Effect of Artificial Hip Arthroplasty: Effect on Promoting Quality of Life and Postoperative Rehabilitation.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Apr 12;2022:1247002. doi: 10.1155/2022/1247002. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jun 28;2023:9845958. doi: 10.1155/2023/9845958. PMID: 35465014 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
-
[Analgesic effect of a new "cocktail" of local infiltration analgesia after total hip arthroplasty-A prospective randomized controlled study].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Dec 15;36(12):1485-1491. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202209003. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36545856 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Effect of Ward-Noise-Reduction Management on the Mental Health and Quality of Life of Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Noise Health. 2024 Apr-Jun 01;26(121):174-179. doi: 10.4103/nah.nah_40_24. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Noise Health. 2024. PMID: 38904819 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Local Vibration Therapy on the Mental State, Neurological Function, and Quality of Life of Convalescing Patients With Spinal Cord Injury.Altern Ther Health Med. 2024 Dec;30(12):18-26. Altern Ther Health Med. 2024. PMID: 38607194
References
-
- Melo-Fonseca F, Miranda G, Domingues HS, Pinto IM, Gasik M, Silva FS. Reengineering bone-implant interfaces for improved mechanotransduction and clinical outcomes. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020;16:1121–38. - PubMed
-
- Zalikha AK, Karabon P, Hajj Hussein I, El-Othmani MM. Anxiety and depression impact on inhospital complications and outcomes after total knee and hip arthroplasty: a propensity score-weighted retrospective analysis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2021;29:873–84. - PubMed
-
- Pan X, Wang J, Lin Z, Dai W, Shi Z. Depression and anxiety are risk factors for postoperative pain-related symptoms and complications in patients undergoing primary total knee arthroplasty in the United States. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34:2337–46. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical