Comprehensive analysis of RNA-5-methylcytosine modification in breast cancer brain metastasis
- PMID: 39345093
- PMCID: PMC11572191
- DOI: 10.1080/14796694.2024.2405459
Comprehensive analysis of RNA-5-methylcytosine modification in breast cancer brain metastasis
Abstract
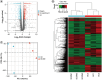
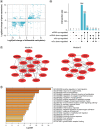
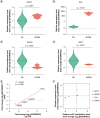
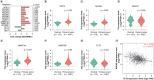
Aim: To delineate the RNA-5-methylcytosine (m5C) modification of breast cancer brain metastasis (BCBM).Methods: Methylated RNA immunoprecipitation next-generation sequencing (MeRIP-seq) was performed to obtain RNA-m5C patterns of BCBM.Results: 1048 hypermethylation and 1866 hypomethylation m5C peaks were identified in BCBM compared with those in breast cancer. The most significant m5C hypermethylated genes included ENG, SHANK1, IGFN1, EVL and MMP9, whereas the most significant m5C hypomethylated genes included AREG, SAA2, TP53I11, KRT7 and LCN2. MeRIP-qPCR data were concordant with the corresponding MeRIP-seq results in terms of the observed m5C levels. Conjoint analysis identified 190 hyper-up genes characterized by concurrent m5C hypermethylation and up-regulation, alongside 284 hypo-down genes exhibiting both m5C hypomethylation and down-regulation.Conclusion: This study presents the first comprehensive analysis of RNA-m5C modification in BCBM.
Keywords: 5-methylcytosine (m5C); breast cancer brain metastasis; methylated RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeRIP-seq); molecular mechanism.
Plain language summary
[Box: see text].
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ZR2022MH272 and ZR2023QH115/Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province
- M-2022122/Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Foundation of Shandong Province
- 202111000399 and 202202080721/Medicine and Health Science and Technology Foundation of Shandong Province
- 81702884/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022YDSF31 and 2022YDSF35/Liaocheng Key R&D Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
