The clinical efficacy of "water-jet" hemostasis in gastrointestinal endoscopic submucosal dissection
- PMID: 39345296
- PMCID: PMC11427691
- DOI: 10.1093/gastro/goae088
The clinical efficacy of "water-jet" hemostasis in gastrointestinal endoscopic submucosal dissection
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the safety and efficacy of "water-jet" hemostasis during endoscopic submucosal dissection.
Methods: In this prospective single-arm clinical study, 10 patients aged 18-60 years with gastric or intestinal mucosal lesions who were admitted to Fujian Medical University Xiamen Humanity Hospital (Xiamen, P. R. China) between June 2022 and June 2023 and met the absolute indications for endoscopic treatment were finally analyzed. The primary outcomes of this study are the incidence rates of adverse events and R0 resection, and the secondary outcomes are length of hospital stay and short- and long-term outcomes.
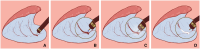
Results: Successful hemostasis was achieved in all the included cases. In one case, the "water-jet" hemostasis failed to stop bleeding in one blood vessel, so the hemostatic forceps were used instead. No adverse events occurred in all cases. Pathologic results showed R0 resection in all samples.
Conclusion: The "water-jet" method is safe and feasible for hemostasis in endoscopic submucosal dissection.
Keywords: bleeding; endoscopic submucosal dissection; hemostasis; “water-jet”.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press and Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric neoplasia with a water jet-assisted knife: a Western, single-center experience.Gastrointest Endosc. 2012 Jun;75(6):1166-74. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2012.02.027. Epub 2012 Apr 5. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012. PMID: 22482915 Clinical Trial.
-
HybridKnife high-pressure glycerol jet injection for endoscopic submucosal dissection increases procedural ease and speed: a randomised study in pigs and a human case series.Surg Endosc. 2016 Jul;30(7):3152-9. doi: 10.1007/s00464-015-4554-6. Epub 2015 Oct 20. Surg Endosc. 2016. PMID: 26487225
-
Management of bleeding and artificial gastric ulcers associated with endoscopic submucosal dissection.World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2012 Jan 16;4(1):1-8. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v4.i1.1. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2012. PMID: 22267977 Free PMC article.
-
AGA Institute Clinical Practice Update: Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in the United States.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Jan;17(1):16-25.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.07.041. Epub 2018 Aug 2. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30077787 Review.
-
Use of water jet instruments in gastrointestinal endoscopy.World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2016 Feb 10;8(3):122-7. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v8.i3.122. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2016. PMID: 26862362 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mochizuki S, Ikeda Y, Arai T. et al. Toward further prevention of bleeding after gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dig Endosc 2015;27:295–7. - PubMed
-
- Libânio D, Costa MN, Pimentel-Nunes P. et al. Risk factors for bleeding after gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc 2016;84:572–86. - PubMed
-
- Pimentel-Nunes P, Libânio D, Bastiaansen BAJ. et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial gastrointestinal lesions: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline—Update 2022. Endoscopy 2022;54:591–622. - PubMed
-
- Zhang ZZ, Zhu CC, Cao H.. Thinking and strategy selection on the quality control of early gastric cancer. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi 2024;27:137–42. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

