Safety and effectiveness of mirabegron for children and adolescents with refractory idiopathic overactive bladder for improving urinary symptoms: a systematic review
- PMID: 39345308
- PMCID: PMC11428357
- DOI: 10.5173/ceju.2023.237
Safety and effectiveness of mirabegron for children and adolescents with refractory idiopathic overactive bladder for improving urinary symptoms: a systematic review
Abstract
Introduction: The aim of this study was to determine the safety and effectiveness of mirabegron in children with refractory overactive bladder (OAB) for improving urinary symptoms.
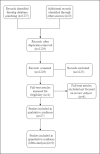
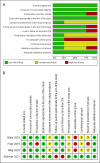
Material and methods: We conducted a search strategy in MEDLINE (OVID), EMBASE, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), and LILACS from inception to September 2023. We performed a systematic review of studies evaluating the effectiveness of improving urinary symptoms and the safety of mirabegron at any dose in children and adolescents with idiopathic refractory OAB. We searched the interception to September 2023. The risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane risk of bias tool for clinical trials and the MINORS tool for non-randomized studies.
Results: We included three studies in the analysis. All of them included children and adolescents receiving mirabegron as monotherapy at different doses. Also, none of them reported a control group. Improvement and safety rates were high in every study in objective and subjective measurements. Compliance was also high in all studies. Most of the evaluated items had a low risk of bias within and across studies.
Conclusions: Mirabegron as monotherapy appears to be a safe and effective alternative for children with refractory idiopathic OAB or those who are intolerant to antimuscarinic therapy.
Keywords: beta-3 agonist; idiopathic overactive bladder; mirabegron; urinary symptoms.
Copyright by Polish Urological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prospective Pilot Study of Mirabegron in Pediatric Patients with Overactive Bladder.Eur Urol. 2016 Jul;70(1):9-13. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.02.007. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Eur Urol. 2016. PMID: 26876327
-
Efficacy and Safety of Combination Pharmacotherapy for Patients with Overactive Bladder: A Rapid Evidence Assessment.Eur Urol. 2019 Dec;76(6):767-779. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.07.010. Epub 2019 Aug 13. Eur Urol. 2019. PMID: 31416636 Review.
-
Mirabegron is alternative to antimuscarinic agents for overactive bladder without higher risk in hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Urol. 2018 Aug;36(8):1285-1297. doi: 10.1007/s00345-018-2268-9. Epub 2018 Mar 19. World J Urol. 2018. PMID: 29556972
-
Mirabegron Add-on Therapy to Tamsulosin for the Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Men with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: A Randomized, Placebo-controlled Study (MATCH).Eur Urol Focus. 2020 Jul 15;6(4):729-737. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2019.10.019. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Eur Urol Focus. 2020. PMID: 31718957 Clinical Trial.
-
The pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of mirabegron in children and adolescents with neurogenic detrusor overactivity or idiopathic overactive bladder and development of a population pharmacokinetic model-based pediatric dose estimation.J Pediatr Urol. 2020 Feb;16(1):31.e1-31.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2019.10.009. Epub 2019 Oct 22. J Pediatr Urol. 2020. PMID: 31787582
Cited by
-
Benzodiazepines use and dependence in female patients with overactive bladder symptoms - prevalence and clinical correlations.Cent European J Urol. 2024;77(4):641-648. doi: 10.5173/ceju.2024.0210. Epub 2024 Nov 16. Cent European J Urol. 2024. PMID: 40313703 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Franco I. Overactive bladder in children. Nature Reviews Urology. 2016; 13: 520-532. - PubMed
-
- Kajiwara M, Inoue K, Kato M, Usui A, Kurihara M, Usui T. Nocturnal enuresis and overactive bladder in children: An epidemiological study. International Journal of Urology. 2006; 13: 36-41. - PubMed
-
- Chung JM, Lee SD, Kang D Il, et al. . Prevalence and Associated Factors of Overactive Bladder in Korean Children 5-13 Years Old: A Nationwide Multicenter Study. Urology. 2009; 73: 63-67. - PubMed
-
- Bartoli S, Aguzzi G, Tarricone R. Impact on Quality of Life of Urinary Incontinence and Overactive Bladder: A Systematic Literature Review. Urology. 2010; 75: 491-500. - PubMed
-
- Landgraf JM, Abidari J, Cilento BG, Cooper CS, Schulman SL, Ortenberg J. Coping, Commitment, and Attitude: Quantifying the Everyday Burden of Enuresis on Children and Their Families. Pediatrics. 2004; 113: 334-344. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources