Chromosomal instability as an architect of the cancer stemness landscape
- PMID: 39345336
- PMCID: PMC11427409
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1450614
Chromosomal instability as an architect of the cancer stemness landscape
Abstract
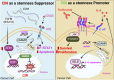
Despite a critical role for tumor-initiating cancer stem cells (CSCs) in breast cancer progression, major questions remain about the properties and signaling pathways essential for their function. Recent discoveries highlighting mechanisms of CSC-resistance to the stress caused by chromosomal instability (CIN) may provide valuable new insight into the underlying forces driving stemness properties. While stress tolerance is a well-known attribute of CSCs, CIN-induced stress is distinctive since levels appear to increase during tumor initiation and metastasis. These dynamic changes in CIN levels may serve as a barrier constraining the effects of non-CSCs and shaping the stemness landscape during the early stages of disease progression. In contrast to most other stresses, CIN can also paradoxically activate pro-tumorigenic antiviral signaling. Though seemingly contradictory, this may indicate that mechanisms of CIN tolerance and pro-tumorigenic inflammatory signaling closely collaborate to define the CSC state. Together, these unique features may form the basis for a critical relationship between CIN and stemness properties.
Keywords: breast cancer; cancer stem cell; chromosomal instability; inflammation; metastasis; stress tolerance.
Copyright © 2024 Baba, Zakeri and Desgrosellier.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Breast cancer stem cells tolerate chromosomal instability during tumor progression via c-Jun/AXL stress signaling.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 14;9(9):e20182. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20182. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37809421 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals the impact of chromosomal instability on glioblastoma cancer stem cells.BMC Med Genomics. 2019 May 31;12(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12920-019-0532-5. BMC Med Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31151460 Free PMC article.
-
Key Roles of Hyaluronan and Its CD44 Receptor in the Stemness and Survival of Cancer Stem Cells.Front Oncol. 2015 Aug 10;5:180. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2015.00180. eCollection 2015. Front Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26322272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of chromosomal instability (CIN) tolerance in aggressive tumors: surviving the genomic chaos.Chromosome Res. 2023 Apr 14;31(2):15. doi: 10.1007/s10577-023-09724-w. Chromosome Res. 2023. PMID: 37058263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of Cdk2 kinase activity selectively targets the CD44⁺/CD24⁻/Low stem-like subpopulation and restores chemosensitivity of SUM149PT triple-negative breast cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2014 Sep;45(3):1193-9. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2523. Epub 2014 Jun 25. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24970653 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cancer Development and Progression Through a Vicious Cycle of DNA Damage and Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 3;26(7):3352. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073352. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40244228 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

