This is a preprint.
The Gq/11 family of Gα subunits is necessary and sufficient for lower jaw development
- PMID: 39345358
- PMCID: PMC11430119
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.09.17.611698
The Gq/11 family of Gα subunits is necessary and sufficient for lower jaw development
Update in
-
The Gq/11 family of Gα subunits is necessary and sufficient for lower jaw development.Development. 2025 Apr 15;152(8):dev204396. doi: 10.1242/dev.204396. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Development. 2025. PMID: 40171762 Free PMC article.
Abstract
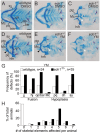
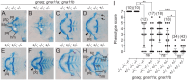
Vertebrate jaw development is coordinated by highly conserved ligand-receptor systems such as the peptide ligand Endothelin 1 (Edn1) and Endothelin receptor type A (Ednra), which are required for patterning of lower jaw structures. The Edn1/Ednra signaling pathway establishes the identity of lower jaw progenitor cells by regulating expression of numerous patterning genes, but the intracellular signaling mechanisms linking receptor activation to gene regulation remain poorly understood. As a first step towards elucidating this mechanism, we examined the function of the Gq/11 family of Gα subunits in zebrafish using pharmacological inhibition and genetic ablation of Gq/11 activity and transgenic induction of a constitutively active Gq protein in edn1 -/- embryos. Genetic loss of Gq/11 activity fully recapitulated the edn1 -/- phenotype, with genes encoding G11 being most essential. Furthermore, inducing Gq activity in edn1 -/- embryos not only restored Edn1/Ednra-dependent jaw structures and gene expression signatures but also caused homeosis of the upper jaw structure into a lower jaw-like structure. These results indicate that Gq/11 is necessary and sufficient to mediate the lower jaw patterning mechanism for Ednra in zebrafish.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; craniofacial development; heterotrimeric G protein; single cell RNA-sequencing; small molecule inhibitor; zebrafish.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The Gq/11 family of Gα subunits is necessary and sufficient for lower jaw development.Development. 2025 Apr 15;152(8):dev204396. doi: 10.1242/dev.204396. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Development. 2025. PMID: 40171762 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinase-mediated cassette exchange reveals the selective use of Gq/G11-dependent and -independent endothelin 1/endothelin type A receptor signaling in pharyngeal arch development.Development. 2008 Feb;135(4):755-65. doi: 10.1242/dev.012708. Epub 2008 Jan 16. Development. 2008. PMID: 18199583
-
Requirements for Endothelin type-A receptors and Endothelin-1 signaling in the facial ectoderm for the patterning of skeletogenic neural crest cells in zebrafish.Development. 2007 Jan;134(2):335-45. doi: 10.1242/dev.02704. Epub 2006 Dec 13. Development. 2007. PMID: 17166927
-
Understanding the basis of auriculocondylar syndrome: Insights from human, mouse and zebrafish genetic studies.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2013 Nov;163C(4):306-17. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31376. Epub 2013 Oct 4. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2013. PMID: 24123988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New perspectives on pharyngeal dorsoventral patterning in development and evolution of the vertebrate jaw.Dev Biol. 2012 Nov 15;371(2):121-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.08.026. Epub 2012 Aug 30. Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22960284 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alexander C., Zuniga E., Blitz I. L., Wada N., Le Pabic P., Javidan Y., Zhang T., Cho K. W., Crump J. G. and Schilling T. F. (2011) Combinatorial roles for BMPs and Endothelin 1 in patterning the dorsal-ventral axis of the craniofacial skeleton. Development 138, 5135–46. doi:10.1242/dev.067801 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aramori I. and Nakanishi S. (1992) Coupling of two endothelin receptor subtypes to differing signal transduction in transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem 267, 12468–74. - PubMed
-
- Barske L., Askary A., Zuniga E., Balczerski B., Bump P., Nichols J. T. and Crump J. G. (2016) Competition between Jagged-Notch and Endothelin1 Signaling Selectively Restricts Cartilage Formation in the Zebrafish Upper Face. PLoS Genet 12, e1005967. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1005967 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
