This is a preprint.
Highly accurate assembly polishing with DeepPolisher
- PMID: 39345401
- PMCID: PMC11429912
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.09.17.613505
Highly accurate assembly polishing with DeepPolisher
Update in
-
Highly accurate assembly polishing with DeepPolisher.Genome Res. 2025 Jul 1;35(7):1595-1608. doi: 10.1101/gr.280149.124. Genome Res. 2025. PMID: 40389286 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Accurate genome assemblies are essential for biological research, but even the highest quality assemblies retain errors caused by the technologies used to construct them. Base-level errors are typically fixed with an additional polishing step that uses reads aligned to the draft assembly to identify necessary edits. However, current methods struggle to find a balance between over-and under-polishing. Here, we present an encoder-only transformer model for assembly polishing called DeepPolisher, which predicts corrections to the underlying sequence using Pacbio HiFi read alignments to a diploid assembly. Our pipeline introduces a method, PHARAOH (Phasing Reads in Areas Of Homozygosity), which uses ultra-long ONT data to ensure alignments are accurately phased and to correctly introduce heterozygous edits in falsely homozygous regions. We demonstrate that the DeepPolisher pipeline can reduce assembly errors by half, with a greater than 70% reduction in indel errors. We have applied our DeepPolisher-based pipeline to 180 assemblies from the next Human Pangenome Reference Consortium (HPRC) data release, producing an average predicted Quality Value (QV) improvement of 3.4 (54% error reduction) for the majority of the genome.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest A.C, D.E.C, P.C., A.K., L.B., M.N. and K.S. are employees of Google LLC and own Alphabet stock as part of the standard compensation package.
Figures
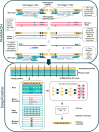



References
-
- Porubsky D, Dashnow H, Sasani TA, et al. A familial, telomere-to-telomere reference for human de novo mutation and recombination from a four-generation pedigree. Published online August 5, 2024:2024.08.05.606142. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.05.606142 - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
