This is a preprint.
Decoding polyubiquitin regulation of KV7. 1 functional expression with engineered linkage-selective deubiquitinases
- PMID: 39345403
- PMCID: PMC11429900
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.09.17.613539
Decoding polyubiquitin regulation of KV7. 1 functional expression with engineered linkage-selective deubiquitinases
Update in
-
Decoding polyubiquitin regulation of KV7. 1 (KCNQ1) surface expression with engineered linkage-selective deubiquitinases.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):5805. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60893-0. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40593673 Free PMC article.
Abstract
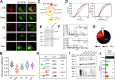
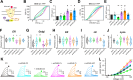
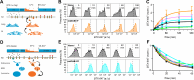
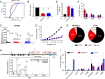
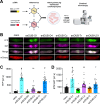
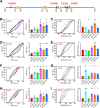
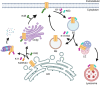
Protein posttranslational modification with distinct polyubiquitin linkage chains is a critical component of the 'ubiquitin code' that universally regulates protein expression and function to control biology. Functional consequences of diverse polyubiquitin linkages on proteins are mostly unknown, with progress hindered by a lack of methods to specifically tune polyubiquitin linkages on individual proteins in live cells. Here, we bridge this gap by exploiting deubiquitinases (DUBs) with preferences for hydrolyzing different polyubiquitin linkages: OTUD1 - K63; OTUD4 - K48; Cezanne - K11; TRABID - K29/K33; and USP21 - non-specific. We developed a suite of engineered deubiquitinases (enDUBs) comprised of DUB catalytic domains fused to a GFP-targeted nanobody and used them to investigate polyubiquitin linkage regulation of an ion channel, YFP-KCNQ1. Mass spectrometry of YFP-KCNQ1 expressed in HEK293 cells indicated channel polyubiquitination with K48 (72%) and K63 (24%) linkages being dominant. NEDD4-2 and ITCH both decreased KCNQ1 functional expression but with distinctive polyubiquitination signatures. All enDUBs reduced KCNQ1 ubiquitination but yielded unique effects on channel expression, surface density, ionic currents, and subcellular localization. The pattern of outcomes indicates K11, K29/K33, and K63 chains mediate net KCNQ1-YFP intracellular retention, but achieved in different ways: K11 promotes ER retention/degradation, enhances endocytosis, and reduces recycling; K29/K33 promotes ER retention/degradation; K63 enhances endocytosis and reduces recycling. The pattern of enDUB effects on KCNQ1-YFP differed in cardiomyocytes, emphasizing ubiquitin code mutability. Surprisingly, enDUB-O4 decreased KCNQ1-YFP surface density suggesting a role for K48 in forward trafficking. Lastly, linkage-selective enDUBs displayed varying capabilities to rescue distinct trafficking-deficient long QT syndrome type 1 mutations. The results reveal distinct polyubiquitin chains control different aspects of KCNQ1 functional expression, demonstrate ubiquitin code plasticity, and introduce linkage-selective enDUBs as a potent tool to help demystify the polyubiquitin code.
Keywords: KCNQ1; deubiquitinase; ion channel; ion channel trafficking; long QT syndrome; polyubiquitin; protein degradation; ubiquitin; ubiquitin code; ubiquitin linkage.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests S.A.K. and H.M.C. are inventors on a patent held by Columbia University for “Compositions and methods for using engineered deubiquitinases for probing ubiquitin-dependent cellular processes.” H.M.C. is a scientific co-founder and on the SAB of two startups, Stablix, Inc. and Flux Therapeutics, pursuing targeted protein stabilization therapeutics. S.A.K. is a co-founder and employee of Stablix, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Decoding polyubiquitin regulation of KV7. 1 (KCNQ1) surface expression with engineered linkage-selective deubiquitinases.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):5805. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60893-0. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40593673 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling chain specific ubiquitination in cells using tandem ubiquitin binding entities.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22961. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07242-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595035 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Nef Antagonizes SERINC5 Restriction by Downregulation of SERINC5 via the Endosome/Lysosome System.J Virol. 2018 May 14;92(11):e00196-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00196-18. Print 2018 Jun 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29514909 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
