This is a preprint.
Cholesterol binding to VCAM-1 promotes vascular inflammation
- PMID: 39345495
- PMCID: PMC11429921
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.09.17.613543
Cholesterol binding to VCAM-1 promotes vascular inflammation
Abstract
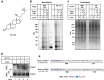
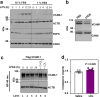
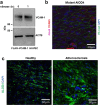
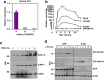
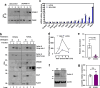
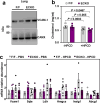
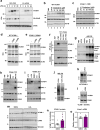
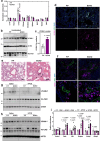
Hypercholesterolemia has long been implicated in endothelial cell (EC) dysfunction, but the mechanisms by which excess cholesterol causes vascular pathology are incompletely understood. Here we used a cholesterol-mimetic probe to map cholesterol-protein interactions in primary human ECs and discovered that cholesterol binds to and stabilizes the adhesion molecule VCAM-1. We show that accessible plasma membrane (PM) cholesterol in ECs is acutely responsive to inflammatory stimuli and that the nonvesicular cholesterol transporter Aster-A regulates VCAM-1 stability in activated ECs by controlling the size of this pool. Deletion of Aster-A in ECs increases VCAM-1 protein, promotes immune cell recruitment to vessels, and impairs pulmonary immune homeostasis. Conversely, depleting cholesterol from the endothelium in vivo dampens VCAM-1 induction in response to inflammatory stimuli. These findings identify cholesterol binding to VCAM-1 as a key step during EC activation and provide a biochemical explanation for the ability of excess membrane cholesterol to promote immune cell recruitment to the endothelium.
Figures




References
-
- Lange Y., Swaisgood M. H., Ramos B. V. & Steck T. L. Plasma membranes contain half the phospholipid and 90% of the cholesterol and sphingomyelin in cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 264, 3786–3793 (1989). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
