This is a preprint.
Craters on the melanoma surface facilitate tumor-immune interactions and demonstrate pathologic response to checkpoint blockade in humans
- PMID: 39345527
- PMCID: PMC11429731
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.09.18.613595
Craters on the melanoma surface facilitate tumor-immune interactions and demonstrate pathologic response to checkpoint blockade in humans
Abstract
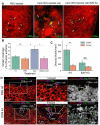
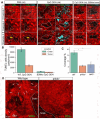
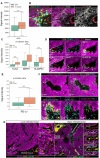
Immunotherapy leads to cancer eradication despite the tumor's immunosuppressive environment. Here, we used extended long-term in-vivo imaging and high-resolution spatial transcriptomics of endogenous melanoma in zebrafish, and multiplex imaging of human melanoma, to identify domains that facilitate immune response during immunotherapy. We identified crater-shaped pockets at the margins of zebrafish and human melanoma, rich with beta-2 microglobulin (B2M) and antigen recognition molecules. The craters harbor the highest density of CD8+ T cells in the tumor. In zebrafish, CD8+ T cells formed prolonged interactions with melanoma cells within craters, characteristic of antigen recognition. Following immunostimulatory treatment, the craters enlarged and became the major site of activated CD8+ T cell accumulation and tumor killing that was B2M dependent. In humans, craters predicted immune response to ICB therapy, showing response better than high T cell infiltration. This marks craters as potential new diagnostic tool for immunotherapy success and targets to enhance ICB response.
Conflict of interest statement
L.I.Z. is a founder and stockholder of Fate Therapeutics, CAMP4 Therapeutics, Amagma Therapeutics, Scholar Rock, and Branch Biosciences. He is a consultant for Celularity and Cellarity. JVA is on the BMS and AstraZeneca advisory board and a consultrant for MSD, Janssen. F.S.H reports grants and personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, personal fees from Merck, grants and personal fees from Novartis, personal fees from Surface, personal fees from Compass Therapeutics, personal fees from Apricity, personal fees from 7 Hills Pharma, personal fees from Bicara, personal fees from Checkpoint Therapeutics, personal fees from Bioentre, personal fees from Gossamer, personal fees from Iovance, personal fees from Catalym, personal fees from Immunocore, personal fees from Kairos, personal fees from Rheos, personal fees from Zumutor, personal fees from Corner Therapeuitcs, personal fees from Puretech, personal fees from Curis, personal fees from Astra Zeneca, personal fees from Solu Therapeutics, outside the submitted work; In addition, Dr. Hodi has a patent Methods for Treating MICA-Related Disorders (#20100111973) with royalties paid, a patent Tumor antigens and uses thereof (#7250291) issued, a patent Angiopoiten-2 Biomarkers Predictive of Anti-immune checkpoint response (#20170248603) pending, a patent Compositions and Methods for Identification, Assessment, Prevention, and Treatment of Melanoma using PD-L1 Isoforms (#20160340407) pending, a patent Therapeutic peptides (#20160046716) pending, a patent Therapeutic Peptides (#20140004112) pending, a patent Therapeutic Peptides (#20170022275) pending, a patent Therapeutic Peptides (#20170008962) pending, a patent THERAPEUTIC PEPTIDES Ðherapeutic PeptidesÐatent number: 9402905 issued, a patent METHODS OF USING PEMBROLIZUMAB AND TREBANANIB pending, a patent Vaccine compositions and methods for restoring NKG2D pathway function against cancers Ðatent number: 10279021 issued, a patent Úntibodies that bind to MHC class I polypeptide-related Sequence A Ð’dÐatent number: 10106611 issued, a patent ÚNTI-GALECTIN ANTIBODY BIOMARKERS PREDICTIVE OF ANTI-IMMUNE CHECKPOINT AND ANTI-ANGIOGENESIS RESPONSES Ð’dÐublication number: 20170343552 pending, and a patent Antibodies against EDIL3 and methods of use thereof pending. JVA: Advisory board: BMS, AstraZeneca Consultant: MSD, Janssen.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Tissue-resident memory T cells from a metastatic vaginal melanoma patient are tumor-responsive T cells and increase after anti-PD-1 treatment.J Immunother Cancer. 2022 May;10(5):e004574. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-004574. J Immunother Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35550554 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing anti-tumor and anti-self immunity in a patient with melanoma receiving immune checkpoint blockade.J Transl Med. 2024 Mar 5;22(1):241. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-04973-7. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38443917 Free PMC article.
-
Clustering by antigen-presenting genes reveals immune landscapes and predicts response to checkpoint immunotherapy.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 18;13(1):950. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-28167-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36653470 Free PMC article.
-
The immune-related role of beta-2-microglobulin in melanoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 16;12:944722. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.944722. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36046045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Lung Cancer Immunotherapy: Input of T-Cell Epitopes Associated With Impaired Peptide Processing.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 3;10:1505. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01505. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31333652 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dobry A.S., Zogg C.K., Hodi F.S., Smith T.R., Ott P.A., and Iorgulescu J.B. (2018). Management of metastatic melanoma: improved survival in a national cohort following the approvals of checkpoint blockade immunotherapies and targeted therapies. Cancer Immunol Immunother 67, 1833–1844. 10.1007/s00262-018-2241-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wolchok J.D., Chiarion-Sileni V., Gonzalez R., Grob J.J., Rutkowski P., Lao C.D., Cowey C.L., Schadendorf D., Wagstaff J., Dummer R., et al. (2022). Long-Term Outcomes With Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab or Nivolumab Alone Versus Ipilimumab in Patients With Advanced Melanoma. J Clin Oncol 40, 127–137. 10.1200/JCO.21.02229. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Magen A., Hamon P., Fiaschi N., Soong B.Y., Park M.D., Mattiuz R., Humblin E., Troncoso L., D’Souza D., Dawson T., et al. (2023). Intratumoral dendritic cell-CD4(+) T helper cell niches enable CD8(+) T cell differentiation following PD-1 blockade in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Med 29, 1389–1399. 10.1038/s41591-023-02345-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
References for methods:
-
- Covassin L.D., Siekmann A.F., Kacergis M.C., Laver E., Moore J.C., Villefranc J.A., Weinstein B.M., and Lawson N.D. (2009). A genetic screen for vascular mutants in zebrafish reveals dynamic roles for Vegf/Plcg1 signaling during artery development. Dev Biol 329, 212–226. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.02.031. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Patton E.E., Widlund H.R., Kutok J.L., Kopani K.R., Amatruda J.F., Murphey R.D., Berghmans S., Mayhall E.A., Traver D., Fletcher C.D., et al. (2005). BRAF mutations are sufficient to promote nevi formation and cooperate with p53 in the genesis of melanoma. Curr Biol 15, 249–254. 10.1016/j.cub.2005.01.031. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
