This is a preprint.
LM-Merger: A workflow for merging logical models with an application to gene regulation
- PMID: 39345612
- PMCID: PMC11429764
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.09.13.612961
LM-Merger: A workflow for merging logical models with an application to gene regulation
Update in
-
LM-Merger: a workflow for merging logical models with an application to gene regulatory network models.BMC Bioinformatics. 2025 Jul 15;26(1):178. doi: 10.1186/s12859-025-06212-2. BMC Bioinformatics. 2025. PMID: 40665244 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Motivation: Gene regulatory network (GRN) models provide mechanistic understanding of genetic interactions that regulate gene expression and, consequently, influence cellular behavior. Dysregulated gene expression plays a critical role in disease progression and treatment response, making GRN models a promising tool for precision medicine. While researchers have built many models to describe specific subsets of gene interactions, more comprehensive models that cover a broader range of genes are challenging to build. This necessitates the development of automated approaches for merging existing models.
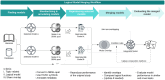
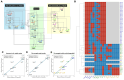
Results: We present LM-Merger, a workflow for semi-automatically merging logical GRN models. The workflow consists of five main steps: (a) model identification, (b) model standardization and annotation, (c) model verification, (d) model merging, and (d) model evaluation. We demonstrate the feasibility and benefit of this workflow with two pairs of published models pertaining to acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The integrated models were able to retain the predictive accuracy of the original models, while expanding coverage of the biological system. Notably, when applied to a new dataset, the integrated models outperformed the individual models in predicting patient response. This study highlights the potential of logical model merging to advance systems biology research and our understanding of complex diseases.
Availability and implementation: The workflow and accompanying tools, including modules for model standardization, automated logical model merging, and evaluation, are available at https://github.com/IlyaLab/LogicModelMerger/.
Keywords: acute myeloid leukemia; gene regulatory networks; logical models; model integration; systems biology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
LM-Merger: a workflow for merging logical models with an application to gene regulatory network models.BMC Bioinformatics. 2025 Jul 15;26(1):178. doi: 10.1186/s12859-025-06212-2. BMC Bioinformatics. 2025. PMID: 40665244 Free PMC article.
-
Hail Lifestyle Medicine consensus position statement as a medical specialty: Middle Eastern perspective.Front Public Health. 2025 Jun 20;13:1455871. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1455871. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40620567 Free PMC article.
-
Perceptions and experiences of the prevention, detection, and management of postpartum haemorrhage: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 27;11(11):CD013795. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013795.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 38009552 Free PMC article.
-
Does the Presence of Missing Data Affect the Performance of the SORG Machine-learning Algorithm for Patients With Spinal Metastasis? Development of an Internet Application Algorithm.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Jan 1;482(1):143-157. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002706. Epub 2023 Jun 12. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 37306629 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Karlebach G, Shamir R. Modelling and analysis of gene regulatory networks. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008. Oct;9(10):770–80. - PubMed
-
- Sgariglia D, Carneiro FRG, Vidal de Carvalho LA, Pedreira CE, Carels N, da Silva FAB. Optimizing therapeutic targets for breast cancer using boolean network models. Comput Biol Chem. 2024. Apr;109:108022. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
