Electron diffraction and solid-state NMR reveal the structure and exciton coupling in a eumelanin precursor
- PMID: 39345764
- PMCID: PMC11423530
- DOI: 10.1039/d4sc05453a
Electron diffraction and solid-state NMR reveal the structure and exciton coupling in a eumelanin precursor
Abstract
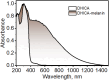
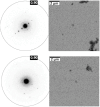
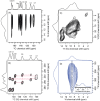
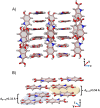
Eumelanin, a versatile biomaterial found throughout the animal kingdom, performs essential functions like photoprotection and radical scavenging. The diverse properties of eumelanin are attributed to its elusive and heterogenous structure with DHI (5,6-dihydroxyindole) and DHICA (5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid) precursors as the main constituents. Despite DHICA being recognized as the key eumelanin precursor, its crystal structure and functional role in the assembled state remain unknown. Herein, we employ a synthesis-driven, bottom-up approach to elucidate the structure and assembly-specifics of DHICA, a critical building block of eumelanin. We introduce an interdisciplinary methodology to analyse the nanocrystalline assembly of DHICA, employing three-dimensional electron diffraction (3D ED), solid-state NMR and density functional theory (DFT), while correlating the structural aspects with the electronic spectroscopic features. The results underscore charge-transfer exciton delocalization as the predominant energy transfer mechanism within the π-π stacked and hydrogen-bonded crystal network of DHICA. Additionally, extending the investigation to the 13C-labelled DHICA-based polymer improves our understanding of the chemical heterogeneity across the eumelanin pigment, providing crucial insights into the structure of eumelanin.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structural Investigation of DHICA Eumelanin Using Density Functional Theory and Classical Molecular Dynamics Simulations.Molecules. 2022 Dec 1;27(23):8417. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238417. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36500509 Free PMC article.
-
Free Energy and Stacking of Eumelanin Nanoaggregates.J Phys Chem B. 2022 Mar 3;126(8):1805-1818. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.1c07884. Epub 2022 Feb 17. J Phys Chem B. 2022. PMID: 35175060
-
Exciton interactions in helical crystals of a hydrogen-bonded eumelanin monomer.Chem Sci. 2022 Jan 27;13(8):2331-2338. doi: 10.1039/d1sc06755a. eCollection 2022 Feb 23. Chem Sci. 2022. PMID: 35310511 Free PMC article.
-
"Fifty Shades" of Black and Red or How Carboxyl Groups Fine Tune Eumelanin and Pheomelanin Properties.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 May 17;17(5):746. doi: 10.3390/ijms17050746. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27196900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melanoma, Melanin, and Melanogenesis: The Yin and Yang Relationship.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 14;12:842496. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.842496. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35359389 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aggregation-assisted energy gap modulation controls delayed emission in hybrid charge-transfer emitters.Chem Sci. 2025 Jul 30. doi: 10.1039/d5sc02071a. Online ahead of print. Chem Sci. 2025. PMID: 40747320 Free PMC article.
-
Larval Pigmentation Reveals Environmental and Genetic Influences in Hybridizing Ambystoma Salamanders.Ecol Evol. 2025 Aug 3;15(8):e71911. doi: 10.1002/ece3.71911. eCollection 2025 Aug. Ecol Evol. 2025. PMID: 40755891 Free PMC article.
-
Solid State NMR for Mechanistic Exploration of CO2 Adsorption on Amine-Based Silica Adsorbents.ACS Omega. 2025 Feb 20;10(8):7485-7492. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c11221. eCollection 2025 Mar 4. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40060837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural disorder as a key to photoprotection in eumelanin multimers.Chem Sci. 2025 Jul 1;16(31):14304-14313. doi: 10.1039/d5sc00920k. eCollection 2025 Aug 6. Chem Sci. 2025. PMID: 40656532 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the Topology of Sitagliptin Using an Integrated Approach.ACS Omega. 2025 Jan 10;10(2):2289-2295. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c09930. eCollection 2025 Jan 21. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 39866596 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen C. T. Chuang C. Cao J. Ball V. Ruch D. Buehler M. J. Nat. Commun. 2014;5:1–10. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

