Expression and Targeted Application of Claudins Family in Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Diseases
- PMID: 39345937
- PMCID: PMC11439345
- DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S483861
Expression and Targeted Application of Claudins Family in Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Diseases
Abstract
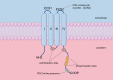
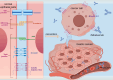
Hepatobiliary and pancreatic diseases are becoming increasingly common worldwide and associated cancers are prone to recurrence and metastasis. For a more accurate treatment, new therapeutic strategies are urgently needed. The claudins (CLDN) family comprises a class of membrane proteins that are the main components of tight junctions, and are essential for forming intercellular barriers and maintaining cellular polarity. In mammals, the claudin family contains at least 27 transmembrane proteins and plays a major role in mediating cell adhesion and paracellular permeability. Multiple claudin proteins are altered in various cancers, including gastric cancer (GC), esophageal cancer (EC), hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), pancreatic cancer (PC), colorectal cancer (CRC) and breast cancer (BC). An increasing number of studies have shown that claudins are closely associated with the occurrence and development of hepatobiliary and pancreatic diseases. Interestingly, claudin proteins exhibit different effects on cancer progression in different tumor tissues, including tumor suppression and promotion. In addition, various claudin proteins are currently being studied as potential diagnostic and therapeutic targets, including claudin-3, claudin-4, claudin-18.2, etc. In this article, the functional phenotype, molecular mechanism, and targeted application of the claudin family in hepatobiliary and pancreatic diseases are reviewed, with an emphasis on claudin-1, claudin-4, claudin-7 and claudin-18.2, and the current situation and future prospects are proposed.
Keywords: cholangiocarcinoma; claudins; hepatocellular carcinoma; pancreatic cancer; targeted therapy.
© 2024 Du et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The claudin family of proteins in human malignancy: a clinical perspective.Cancer Manag Res. 2013 Nov 8;5:367-75. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S38294. Cancer Manag Res. 2013. PMID: 24232410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role and mechanism of claudins in cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 22;12:1051497. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1051497. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36620607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma invasion by suppression of claudin-10 in HLE cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Nov;6(11):2858-67. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0453. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007. PMID: 18025272
-
Claudin and pancreatic cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 7;13:1136227. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1136227. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36959784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Claudins and hepatocellular carcinoma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Feb;171:116109. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.116109. Epub 2024 Jan 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38185042 Review.
References
-
- Li Q, Xia C, Li H, et al. Disparities in 36 cancers across 185 countries: secondary analysis of global cancer statistics. Front Med. 2024;2024:1. - PubMed
-
- Balda MS, Whitney JA, Flores C, González S, Cereijido M, Matter K. Functional dissociation of paracellular permeability and transepithelial electrical resistance and disruption of the apical-basolateral intramembrane diffusion barrier by expression of a mutant tight junction membrane protein. J Cell Biol. 1996;134(4):1031–1049. doi:10.1083/jcb.134.4.1031 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous