Regulatory elements in SEM1-DLX5-DLX6 (7q21.3) locus contribute to genetic control of coronal nonsyndromic craniosynostosis and bone density-related traits
- PMID: 39345948
- PMCID: PMC11434253
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gimo.2024.101851
Regulatory elements in SEM1-DLX5-DLX6 (7q21.3) locus contribute to genetic control of coronal nonsyndromic craniosynostosis and bone density-related traits
Abstract
Purpose: The etiopathogenesis of coronal nonsyndromic craniosynostosis (cNCS), a congenital condition defined by premature fusion of 1 or both coronal sutures, remains largely unknown.
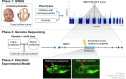
Methods: We conducted the largest genome-wide association study of cNCS followed by replication, fine mapping, and functional validation of the most significant region using zebrafish animal model.
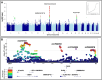
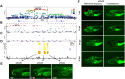
Results: Genome-wide association study identified 6 independent genome-wide-significant risk alleles, 4 on chromosome 7q21.3 SEM1-DLX5-DLX6 locus, and their combination conferred over 7-fold increased risk of cNCS. The top variants were replicated in an independent cohort and showed pleiotropic effects on brain and facial morphology and bone mineral density. Fine mapping of 7q21.3 identified a craniofacial transcriptional enhancer (eDlx36) within the linkage region of the top variant (rs4727341; odds ratio [95% confidence interval], 0.48[0.39-0.59]; P = 1.2E-12) that was located in SEM1 intron and enriched in 4 rare risk variants. In zebrafish, the activity of the transfected human eDlx36 enhancer was observed in the frontonasal prominence and calvaria during skull development and was reduced when the 4 rare risk variants were introduced into the sequence.
Conclusion: Our findings support a polygenic nature of cNCS risk and functional role of craniofacial enhancers in cNCS susceptibility with potential broader implications for bone health.
Keywords: Coronal Nonsyndromic; Craniosynostosis; DLX6 DLX5; GWAS; Regulatory elements; SEM1.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare no competing interests in relation to the work described.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
- R01 DE030596/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE016886/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DD001223/DD/NCBDD CDC HHS/United States
- CDP 13-003/HX/HSRD VA/United States
- U01 DE024448/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- EP-D-18-001/EPA/EPA/United States
- S10 OD026880/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DD001035/DD/NCBDD CDC HHS/United States
- U01 DD001227/DD/NCBDD CDC HHS/United States
- UL1 TR004419/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN275201100001I/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD030463/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- HHSN275201100001C/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DD001226/DD/NCBDD CDC HHS/United States
- R03 DE031061/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DD001302/DD/NCBDD CDC HHS/United States
- R01 DD000350/DD/NCBDD CDC HHS/United States
- P01 HD078233/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- N01 DK073431/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN275201100001G/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

