Genome-wide identification of the GATA gene family in melon (Cucumis melo) and analysis of their expression characteristics under biotic and abiotic stresses
- PMID: 39345983
- PMCID: PMC11427367
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1462924
Genome-wide identification of the GATA gene family in melon (Cucumis melo) and analysis of their expression characteristics under biotic and abiotic stresses
Abstract
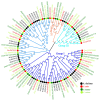
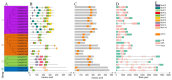
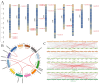
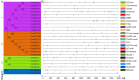
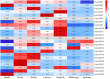
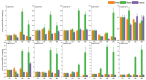
GATA transcription factors are an important class of transcription factors in plants, known for their roles in tissue development, signal transduction, and responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. To date, there have been no reports on the GATA gene family in melon (Cucumis melo). In this study, 24 CmGATA genes were identified from the melon genome. These family members exhibit significant differences in protein length, molecular weight, and theoretical isoelectric point and are primarily located in the nucleus. Based on the classification of Arabidopsis thaliana GATA members, the phylogenetic tree divided them into four groups: group I, group II, group III, and group IV, containing 10, 8, 4, and 2 genes, respectively. Notably, CmGATA genes within the same group have highly conserved protein motifs and similar exon-intron structures. The CmGATA family members are unevenly distributed across 10 chromosomes, with six pairs of segmentally duplicated genes and one pair of tandemly duplicated genes, suggesting that gene duplication may be the primary factor in the expansion of the CmGATA family. Melon shares 21, 4, 38, and 34 pairs of homologous genes with A. thaliana, Oryza sativa, Cucumis sativus, and Citrullus lanatus, respectively. The promoter regions are enriched with various cis-acting elements related to growth and development (eight types), hormone regulation (nine types), and stress responses (six types). Expression patterns indicate that different CmGATA family members are significantly expressed in seeds, roots, stems, leaves, tendrils, mesocarp, and epicarp, exhibiting distinct tissue-specific expression characteristics. Quantitative fluorescence analysis revealed that five genes, CmGATA3, CmGATA7, CmGATA16, CmGATA22, and CmGATA24, may be highly active under 48-h drought stress, while CmGATA1 and CmGATA22 may enhance melon resistance to heavy metal lead stress. Additionally, CmGATA22 and CmGATA24 are suggested to regulate melon resistance to Fusarium wilt infection. CmGATA22 appears to comprehensively regulate melon responses to both biotic and abiotic stresses. Lastly, potential protein interaction networks were predicted for the CmGATA family members, identifying CmGATA8 as a potential hub gene and predicting 2,230 target genes with enriched GO functions. This study preliminarily explores the expression characteristics of CmGATA genes under drought stress, heavy metal lead stress, and Fusarium wilt infection, providing a theoretical foundation for molecular mechanisms in melon improvement and stress resistance.
Keywords: Cucumis melo; Fusarium wilt infection; GATA gene family; drought stress; heavy metal lead stress.
Copyright © 2024 Zheng, Tang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of C3H gene family in melon.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Mar 13;16:1500429. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1500429. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40182554 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of the OMT gene family in Cucumis melo L. and expression analysis under abiotic and biotic stress.PeerJ. 2023 Dec 14;11:e16483. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16483. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 38107581 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of CCD Gene Family in Six Cucurbitaceae Species and Its Expression Profiles in Melon.Genes (Basel). 2022 Jan 28;13(2):262. doi: 10.3390/genes13020262. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205307 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Markers for Marker-Assisted Breeding for Biotic and Abiotic Stress in Melon (Cucumis melo L.): A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 7;25(12):6307. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126307. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Scoping Review on Cucumis melo and Its Anti-Cancer Properties.Malays J Med Sci. 2024 Aug;31(4):63-77. doi: 10.21315/mjms2024.31.4.5. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Malays J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39247112 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification, phylogenetic and expression pattern analysis of GATA gene family in Cerasus humilis.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jun 5;16:1596930. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1596930. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40538883 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of amino acid sequence level in plant GATA transcription factors.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 30;14(1):29786. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81159-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39616200 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of GATA Gene Family in Dendrobium officinale Under Methyl Jasmonate and Salt Stress.Plants (Basel). 2025 May 22;14(11):1576. doi: 10.3390/plants14111576. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40508251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Castro-Mondragon J. A., Riudavets-Puig R., Rauluseviciute I., Lemma R. B., Turchi L., Blanc-Mathieu R., et al. . (2022). JASPAR 2022: the 9th release of the open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 50, D165–D173. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1113 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

