Distally Based Lymphatic Microsurgical Preventive Healing Approach-A Modification of the Classic Approach
- PMID: 39346002
- PMCID: PMC11436324
- DOI: 10.1055/a-2336-0150
Distally Based Lymphatic Microsurgical Preventive Healing Approach-A Modification of the Classic Approach
Abstract
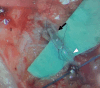
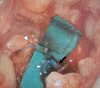
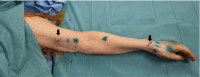
The treatment of breast cancer has seen great success in the recent decade. With longer survivorship, more attention is paid to function and aesthetics as integral treatment components. However, breast cancer-related lymphedema (BCRL) remains a significant complication. Immediate lymphatic reconstruction is an emerging technique to reduce the risk of BCRL, the Lymphatic Microsurgical Preventive Healing Approach (LYMPHA) being the most widely used approach. Despite promising results, it is often difficult to find suitably sized recipient venules and perform the microanastomoses between mismatched vessels deep in the axilla. Moreover, high axillary venous pressure gradients and potential damage from radiotherapy may affect the long-term patency of the anastomoses. From an ergonomic point of view, performing lymphaticovenular anastomosis in the deep axilla may be challenging for the microsurgeon. In response to these limitations, we modified the technique by moving the lymphatic reconstruction distally-terming it distally based LYMPHA (dLYMPHA). A total of 113 patients underwent mastectomy with axillary clearance in our institution from 2018 to 2021. Of these, 26 underwent subsequent dLYMPHA (Group 2), whereas 87 did not (Group 1). In total, 17.2% (15 patients) and 3.84% (1 patient) developed BCRL in Groups 1 and 2, respectively ( p = 0.018). Lymphatics and recipient venules suitable for anastomoses can be reliably found in the distal upper limb with better size match. A distal modification achieves a more favorable lymphaticovenular pressure gradient, vessel match, and ergonomics while ensuring a comparably low BCRL rate.
Keywords: breast cancer; lymphedema; lymphovenous anastomosis; microsurgery.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, permitting unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction so long as the original work is properly cited. ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Johnson A R, Kimball S, Epstein Set al.Lymphedema incidence after axillary lymph node dissection: quantifying the impact of radiation and the lymphatic microsurgical preventive healing approach Ann Plast Surg 201982(4S Suppl 3):S234–S241. - PubMed
-
- Boccardo F M, Casabona F, Friedman D et al.Surgical prevention of arm lymphedema after breast cancer treatment. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18(09):2500–2505. - PubMed
-
- Friedman R, Spiegel D Y, Kinney J, Willcox J, Recht A, Singhal D. Quantifying radiation in the axillary bed at the site of lymphedema surgical prevention. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2023;201(02):299–305. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

