Relationship of Glymphatic Function with Cognitive Impairment, Sleep Disorders, Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 39346025
- PMCID: PMC11439361
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S480183
Relationship of Glymphatic Function with Cognitive Impairment, Sleep Disorders, Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
Introduction: Previous studies have predominantly explored the relationship of the glymphatic system with motor symptoms in Parkinson's disease (PD); however, research on non-motor symptoms remains limited. Therefore, this study investigated the association between glymphatic function and non-motor symptoms, including cognitive impairment and sleep disorders, in PD patients.
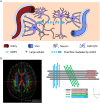
Methods: This study recruited 49 PD patients and 38 healthy controls (HC). Glymphatic function was evaluated using enlarged perivascular spaces (EPVS) in the basal ganglia (BG) region and diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) index. Cognition, sleep, anxiety, and depression scales were assessed in all participants. According to the scale scores, PD patients were further divided into several groups to identify the presence of non-motor symptoms. Differences in EPVS numbers and ALPS index between PD subgroups and HC group were compared. Spearman correlation analysis was performed to investigate the association between the PD non-motor symptoms and ALPS index. Additionally, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves analysis was conducted for ALPS index to predict cognitive impairment and insomnia in PD patients.
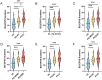
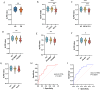
Results: PD patients with and without non-motor symptoms all showed more EPVS numbers than the controls, and the EPVS numbers in PD patients with cognitive impairment were also greater than those without. Notably, except for the depression subgroup, PD patients with non-motor symptoms showed significantly lower ALPS index than the controls. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) scores were positively correlated, whereas the Parkinson's Disease Sleep Scale (PDSS)-2 and REM Sleep Behavior Disorder Screening Questionnaire (RBDSQ) scores were negatively correlated with the ALPS index in PD patients (r=0.3618, P=0.0053; r=-0.4146, P=0.0015; r=-0.2655, P=0.0326, respectively). The ALPS index proved to be predictive of cognitive impairment and insomnia in PD patients (AUC=0.7733, P=0.001; AUC=0.7993, P=0.0004, respectively).
Conclusion: Glymphatic function is closely associated with cognition and sleep of PD patients.
Keywords: cognition; glymphatic system; non-motor symptoms; parkinson’s disease; sleep.
© 2024 Gui et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ryu DW, Yoo SW, Choi KE, Oh YS, Kim JS. Correlation of olfactory function factors with cardiac sympathetic denervation in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol. 2023. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

