Morphometric analysis of the skull base and palatal regions for gender identification using CBCT: a retrospective study
- PMID: 39346032
- PMCID: PMC11430163
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.18127
Morphometric analysis of the skull base and palatal regions for gender identification using CBCT: a retrospective study
Abstract
Objectives: The objectives of this study were to evaluate the accuracy of morphometry of skull base and palate in gender discrimination using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scanning and to assess the accuracy of the results among a sample of the Arab population.
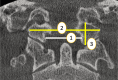
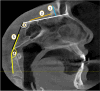
Materials & methods: Using CBCT scans, a cross-sectional analysis was conducted on 142 consented patients who underwent various dental procedures at the University Dental Hospital, Sharjah (UDHS). Of these patients, 70 were females and 72 were males, with respective means of 38.5 and 36.2 years. Eleven parameters related to skull base and palatal region were measured on the CBCT scans by two expert radiologists followed by statistical analysis.
Results: There was significant gender-based difference in the mean palatal width (PW) (p = 0.001), mean palatal height (PH) (p = 0.005). Among other skull base region parameters that were significant in term of gender-based difference like; the clivus length (CL) (p < 0.001), occipital condyle height (OCH) (p < 0.001), basal angle (BA) (p = 0.006) and transverse diameter of foramen magnum (p = 0.003). Only palate variables showed a significant age difference. Discriminant analysis related to gender showed that occipital condyle height was the most accurate and best discriminator among the skull base region parameters.
Conclusion: The use of discriminant analysis in CBCT based on skull base and palatal region variables provides an efficient method for determining gender, which is particularly valuable in forensic science and anthropological research.
Significance of study: Accurate gender identification is crucial in forensic investigations, and the skull base region, being a stable and sexually dimorphic anatomical feature, can serve as a reliable marker for this purpose.
Keywords: Cone beam computed tomography; Discrminant analysi; Sexing; Skull base.
©2024 Uthman et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Abdel-Karim RI, Housseini AM, Hashish RK. Adult sex estimation using three dimensional volume rendering multislice computed tomography of the foramen magnum and occipital condyles: a study in Egyptian population. International Journal of Advanced Research. 2015;3:1212–1215.
-
- Abo El-Atta HM, Abdel-Rahman RH, El-Hawary G, Abo El-Al-Atta HM. Sexual dimorphism of foramen magnum: an Egyptian study. Egyptian Journal of Forensic Sciences. 2020;10(1):1–12. doi: 10.1186/s41935-019-0167-x. - DOI
-
- Ajanovic Z, Dervisevic L, Dervisevic A, Sarac-Hadzihalilovic A, Dervisevic E, Biscević Tokic J, Salihbegovic A, Jugo A, Aganovic I, Prasko S. Sex prediction by geometric morphometric analysis of the hard palate. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 2022;26(17):6057–6064. - PubMed
-
- Aksoy S, Kelahmet U, Hincal E, Oz U, Orhan K. Comparison of linear and angular measurements in CBCT scans using 2D and 3D rendering software. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment. 2016;30(4):777–784. doi: 10.1080/13102818.2016.1174077. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

