Pulsed sounds caused by internal oxygen transport during photosynthesis in the seagrass Halophila ovalis
- PMID: 39346068
- PMCID: PMC11439383
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.18114
Pulsed sounds caused by internal oxygen transport during photosynthesis in the seagrass Halophila ovalis
Abstract
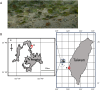
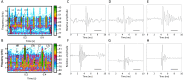
Oxygen bubbles that leak from seagrass blades during photosynthesis have been hypothesized to cause cavitation sounds in aquatic plants. Here we investigate low-amplitude sounds with regular pulse rates produced during photosynthesis in seagrass beds of Halophila ovalis (Qitou Bay, Penghu islands and Cigu Lagoon, Taiwan). Sound pulses appear in the morning when illumination exceeds 10,000 Lux, peak at midday and decrease in midafternoon on a sunny day. Frequencies peak between 1 to 4 kHz, durations range between ca. 1.8 to 4.8 ms, and sound pressure level 1 cm from the bed is 105.4 ± 0.5 dB re 1 μPa (1100 h on a cloudy day). Sounds attenuate rapidly with distance, disappearing beyond 15 cm. Blocking sunlight or administering herbicide stops ongoing sounds. Gas bubbles are not typically seen during sound production ruling out cavitation, and external force (scissor cutting or plant pressed against the substrate) applied to the patch, leaves, petioles, or rhizomes generally increases pulse rate. We suggest sound emission is caused by internal oxygen transport through pores in diaphragms (a whistle mechanism) at the leaf base and nodes of the rhizome.
Keywords: Aerodynamic sounds; Bubble; Halophila ovalis; Internal oxygen transportation; Phytoacoustics; Sound production.
© 2024 Mok et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Richard G. Gilmore, Jr. is employed by Estuarine, Coastal and Ocean Science, Inc., Florida, U.S.A.
Figures


References
-
- Armstrong W. Aeration in higher plants. Advances in Botanical Research. 1979;7:225–332. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2296(08)60089-0. - DOI
-
- Borum J, Sand-Jesen K, Binzer T, Pedersen O, Greve TM. Oxygen movement in seagrasses. In: Larkum AWD, et al., editors. Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation. Dordrecht: Springer; 2006. pp. 255–270.
-
- Felisberto P, Jesus SM, Zabel F, Santos R, Silva J, Gobert S, Beer S, Bjork M, Mazzuca S, Procaccini G, Runcie JW, Champenois W, Borges A. Acoustic monitoring of O2 production of a seagrass meadow. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology. 2015a;464(1):75–87. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2014.12.013. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

