Spatio-temporal modeling of co-dynamics of smallpox, measles, and pertussis in pre-healthcare Finland
- PMID: 39346083
- PMCID: PMC11439382
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.18155
Spatio-temporal modeling of co-dynamics of smallpox, measles, and pertussis in pre-healthcare Finland
Abstract
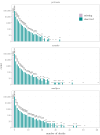
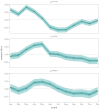
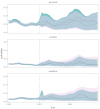
Infections are known to interact as previous infections may have an effect on risk of succumbing to a new infection. The co-dynamics can be mediated by immunosuppression or modulation, shared environmental or climatic drivers, or competition for susceptible hosts. Research and statistical methods in epidemiology often concentrate on large pooled datasets, or high quality data from cities, leaving rural areas underrepresented in literature. Data considering rural populations are typically sparse and scarce, especially in the case of historical data sources, which may introduce considerable methodological challenges. In order to overcome many obstacles due to such data, we present a general Bayesian spatio-temporal model for disease co-dynamics. Applying the proposed model on historical (1820-1850) Finnish parish register data, we study the spread of infectious diseases in pre-healthcare Finland. We observe that measles, pertussis, and smallpox exhibit positively correlated dynamics, which could be attributed to immunosuppressive effects or, for example, the general weakening of the population due to recurring infections or poor nutritional conditions.
Keywords: Bayesian analysis; Infection co-dynamics; Measles; Pertussis; Smallpox; Spatio-temporal.
©2024 Pasanen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Bai J, Wang P. Identification and Bayesian estimation of dynamic factor models. Journal of Business & Economic Statistics. 2015;33(2):221–240. doi: 10.1080/07350015.2014.941467. - DOI
-
- Banner KM, Irvine KM, Rodhouse TJ. The use of Bayesian priors in ecology: the good, the bad and the not great. Methods in Ecology and Evolution. 2020;11(8):882–889. doi: 10.1111/2041-210X.13407. - DOI
-
- Betancourt M. A conceptual introduction to hamiltonian Monte Carlo. 20181701.02434
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

