Design, synthesis, and high-throughput in vitro anti-cancer evaluation of novel 4-aminopyrazolo[3,4- d]pyrimidine derivatives: potential anti-cancer candidates against UO-31 renal cancer cells
- PMID: 39346525
- PMCID: PMC11428193
- DOI: 10.1039/d4ra05136j
Design, synthesis, and high-throughput in vitro anti-cancer evaluation of novel 4-aminopyrazolo[3,4- d]pyrimidine derivatives: potential anti-cancer candidates against UO-31 renal cancer cells
Abstract
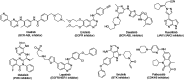
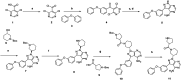
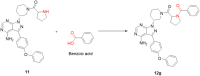
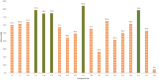
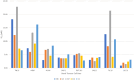
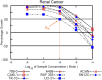
A novel series of 20 compounds containing 4-aminopyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine core were synthesized, characterized and their chemical structures confirmed using spectroscopic techniques such as 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, and HRMS. The compound's growth inhibitory activities were evaluated against 60 human tumor cell lines from nine panels: leukemia, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), colon, central nervous system (CNS), melanoma, ovarian, renal, prostate, and breast cancer. Among all the compounds, 11, 12c, 12d, 12f, and 12j are active against different cancer cell lines. Between all the cell lines, compounds 12c, 12d, 12f, 12j, and 11 showed good inhibitory activity against renal cancer cell lines. From the five-dose study, based on IC50 values, the order of activity of compounds against renal cancer cell lines was found to be 12c > 12f > 12c > 12j > 11 with 12c being the most potent, was better than sunitinib and sorafenib. Having been recognized as initial hits, these substances need additional pharmacological investigation.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isolation and identification of novel selective antitumor constituents, sidrin and sidroside, from Zizyphus spina-christi.Saudi Pharm J. 2023 Jun;31(6):1019-1028. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.04.029. Epub 2023 May 6. Saudi Pharm J. 2023. PMID: 37234346 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Synthesis, and Characterization of Novel Thiazolidine-2,4-Dione-Acridine Hybrids as Antitumor Agents.Molecules. 2024 Jul 18;29(14):3387. doi: 10.3390/molecules29143387. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39064964 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidines as Potential Cytotoxic Agents: Design, Synthesis, Molecular Docking and CDK2 Inhibition.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019;19(11):1368-1381. doi: 10.2174/1871520619666190417153350. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31038080
-
Discovery of novel indolyl-1,2,4-triazole hybrids as potent vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) inhibitors with potential anti-renal cancer activity.Bioorg Chem. 2020 Dec;105:104330. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104330. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 33038552
-
Synthesis, anticancer activity and effects on cell cycle profile and apoptosis of novel thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine and thieno[3,2-e] triazolo[4,3-c]pyrimidine derivatives.Eur J Med Chem. 2015 Jan 27;90:620-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.12.009. Epub 2014 Dec 6. Eur J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25499930
References
-
- Cancer (IARC) TIA for R on Global Cancer Observatory, accessed April 30, 2024, https://gco.iarc.fr/
-
- Global cancer burden growing, amidst mounting need for services, accessed April 30, 2024, https://www.who.int/news/item/01-02-2024-global-cancer-burden-growing--a... - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

