Involvement of Root Canal Treatment in Pro-Inflammatory Processes - A Real-World Study
- PMID: 39346572
- PMCID: PMC11438457
- DOI: 10.2147/POR.S479124
Involvement of Root Canal Treatment in Pro-Inflammatory Processes - A Real-World Study
Abstract
Purpose: Endodontic inflammation typically results from root canal infections and sensitizations to filling materials after root canal treatment (RCT), potentially leading to systemic inflammation and disease. We therefore aimed to characterize the inflammatory alterations after RCT as well as the inflammatory molecule levels following tooth extraction or renewed RCT.
Patients and methods: All (a total of 2585) walk-in patients with or without RCT history were included in this retrospective study. During the 3-year observation period, blood levels of RANTES/CCL5 (regulated on activation, normal T-cell expressed and secreted/chemotactic cytokine ligand 5), C-reactive protein (CRP), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interferon-γ (IFN-γ), and interleukin-10 (IL-10) were measured before and after tooth extraction or renewed RCT. Control patients did not undergo any dental treatment.
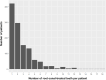
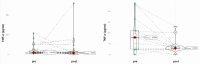
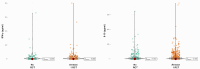
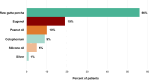
Results: A total 49.38% of patients had a history of at least one RCT. In RCT patients, RANTES/CCL5 values were significantly reduced by both tooth extraction (p=0.03) and renewed dental RCT (p=0.038), while a non-significant increase was observed in untreated patients. TNF-α levels were reduced by tooth extraction (p=0.014) but not by renewed RCT and no intervention. CRP levels were not significantly changed by either treatment. Tooth extraction significantly lowered IFN-γ levels (p=0.003), while in control patients, IFN-γ levels did not change. IL-10 levels were non-significantly reduced by tooth extraction (p=0.061). In a subcohort of RCT patients, the lymphocyte transformation test revealed an allergic reaction to at least one of the root filling materials in 39.46% of patients, with raw gutta percha (56%) and eugenol (19%) being frequent triggers.
Conclusion: Here, we demonstrate the involvement of root-treated teeth in inflammatory processes, as tooth extraction and renewed RCT could significantly reduce individual cytokine levels. Our data support the use of biomarkers for in vivo monitoring of treatment success.
Keywords: RANTES/CCL5; endodontically treated teeth; inflammation; root canal; root canal filling materials; thioether/mercaptans.
© 2024 Diederich and Müller.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Kurt Müller reports personal fees from Dresden International University, personal fees from Institut für Funktionelle Medizin, personal fees from Biovis Laboratory Limburg, outside the submitted work. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
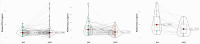


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

