Association between weight-adjusted waist circumference index and depression in older patients with hypertension: a study based on NHANES 2007-2016
- PMID: 39346588
- PMCID: PMC11427274
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1461300
Association between weight-adjusted waist circumference index and depression in older patients with hypertension: a study based on NHANES 2007-2016
Abstract
Objective: Our aim was to assess the relationship between weight-adjusted waist circumference index (WWI) and the prevalence of depression in older adult hypertensive patients in the United States.
Methods: We selected individuals from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database from 2007 to 2016 and used logistic regression analyses, subgroup analyses, and dose-response curves to assess the associations between the WWI index and the prevalence of depression in older hypertensive patients with age, sex, and BMI.
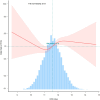
Results: A total of 4,228 participants aged ≥60 years with hypertension were included in our study; 364 patients were assessed for depression. After correction for confounders, each unit increase in WWI increased the risk of depression in older hypertensive patients by 19% (OR = 1.19, 95% CI: 0.99, 1.43). Dose-response curves showed that the WWI index was positively associated with the prevalence of depression in older hypertensive patients when the WWI index was ≥11.6. Based on subgroup analyses, this association was particularly pronounced in individuals ≥70 years of age, women, and individuals with a BMI of 25 or greater.
Conclusion: Higher WWI scores were positively associated with the prevalence of depression in older hypertensive patients and correlated with gender, age and BMI. This is notable, although a causal relationship cannot be established at this time.
Keywords: NHANES; WWI index; cross-sectional study; depression; hypertension in the older adult.
Copyright © 2024 Niu, Sun, Xie and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Association of weight-adjusted waist index with hyperuricemia and gout among middle-aged and older adults in America: a cross-sectional analysis of NHANES 2007-2014.Clin Rheumatol. 2024 Aug;43(8):2615-2626. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07011-5. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Clin Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38861229
-
Association between weight-adjusted waist index and overactive bladder syndrome among adult women in the United States: a cross-sectional study.BMC Womens Health. 2024 Sep 4;24(1):488. doi: 10.1186/s12905-024-03339-x. BMC Womens Health. 2024. PMID: 39232696 Free PMC article.
-
U-shaped Association Between Weight-Adjusted-Waist Index and Arterial Stiffness Among Adult Hypertensive Patients: A Population-Based Study in the United States.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2024 Dec;26(12):1441-1448. doi: 10.1111/jch.14914. Epub 2024 Oct 15. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2024. PMID: 39403045 Free PMC article.
-
Weight-adjusted-waist index is associated with urinary albumin-creatinine ratio in normal body mass index adults: a cross-sectional study from NHANES 2001-2018.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 18;15(1):13459. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-98109-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40251228 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Weight-Adjusted Waist Index and depressive symptoms: A nationally representative cross-sectional study from NHANES 2005 to 2018.J Affect Disord. 2024 Apr 1;350:49-57. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.01.104. Epub 2024 Jan 12. J Affect Disord. 2024. PMID: 38220117 Review.
Cited by
-
U-shaped association between average daily sleep duration and depression among individuals with hypertension: a cross-sectional study based on NHANES 2017-2020.BMC Psychiatry. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):608. doi: 10.1186/s12888-025-07075-w. BMC Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40597928 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Weight-Adjusted Waist Index and Depressive Symptoms Among Middle-Aged and Older Adults: Evidence From Two Prospective Longitudinal Cohort Studies.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Jul;31(7):e70496. doi: 10.1111/cns.70496. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40589318 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Life's Crucial 9 and Cardiorenal syndrome: the mediating role of weight-adjusted-waist index.Front Nutr. 2025 May 27;12:1560224. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1560224. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40497026 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Life's Crucial 9 and overactive bladder: the mediating role of weight-adjusted-waist index.Front Nutr. 2025 Jan 6;11:1508062. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1508062. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39834451 Free PMC article.
-
The curvilinear relationship between Framingham Steatosis Index and depression: insights from a nationwide study.Front Psychiatry. 2025 Jan 31;15:1510327. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1510327. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39957754 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rajati F, Hamzeh B, Pasdar Y, Safari R, Moradinazar M, Shakiba E, et al. . Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension and their determinants: results from the first cohort of non-communicable diseases in a Kurdish settlement. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:12409. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48232-y, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

