A Full Good Manufacturing Practice-Compliant Protocol for Corneal Stromal Stem Cell Cultivation
- PMID: 39346761
- PMCID: PMC11427334
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5074
A Full Good Manufacturing Practice-Compliant Protocol for Corneal Stromal Stem Cell Cultivation
Abstract
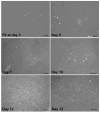
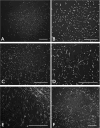
Corneal scarring, a significant cause of global blindness, results from various insults, including trauma, infections, and genetic disorders. The conventional treatment to replace scarred corneal tissues includes partial or full-thickness corneal transplantation using healthy donor corneas. However, only 1 in 70 individuals with treatable corneal scarring can undergo surgery, due to the limited supply of transplantable donor tissue. Our research focuses on cell-based strategies, specifically ex vivo-expanded corneal stromal stem cells (CSSCs), to address corneal scarring. Preclinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of CSSC treatment in reducing corneal inflammation and fibrosis, inhibiting scar formation, and regenerating native stromal tissue. Mechanisms include CSSC differentiation into stromal keratocytes and the expression of regenerative cytokines. Here, we present a good manufacturing practice (GMP)-compliant protocol to isolate and expand human CSSCs. This method paves the way to produce clinical-grade CSSCs for transplantation and clinical trials. Key features • This protocol utilizes surgical skills to dissect human corneal tissues for CSSC isolation. • The yield and features of CSSCs rely on donor tissue quality (freshness) and have donor-to-donor variability. • Up to 0.5 billion CSSCs can be generated from a single cornea specimen, and cells at passage 3 are suitable for treatment uses.
Keywords: Anterior limbal stroma; Corneal opacities; Corneal stromal stem cells; Good manufacturing practices; Standard operating protocol.
©Copyright : © 2024 The Authors; This is an open access article under the CC BY license.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Jeng B. H. and Ahmad S.(2021). In Pursuit of the Elimination of Corneal Blindness: Is Establishing Eye Banks and Training Surgeons Enough? Ophthalmology. 128(6): 813-815. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

