Scutellarein treats neuroblastoma by regulating the expression of multiple targets
- PMID: 39346787
- PMCID: PMC11427791
- DOI: 10.1002/ibra.12100
Scutellarein treats neuroblastoma by regulating the expression of multiple targets
Abstract
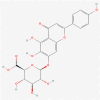
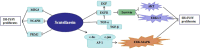
The aim of this study is to investigate the effect of scutellarein on the proliferation of neuroblastoma cells and the underlying mechanism. Six cell lines were used with drug intervention. Cell Counting Kit-8 was used to select the best, namely, SH-SY5Y, and then its IC50 value was determined. To further investigate the mechanism of scutellarin affecting SH-SY5Y proliferation, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was used to detect the expression levels of 11 factors. Scutellarin administration with 300 μM significantly reduced the number of SH-SY5Y, especially on the 3rd day of exposure to scutellarin. The IC50 value of scutellarin in SH-SY5Y cells was determined to be 117.8 μM. But the practical results showed that 300 μM was the optimal concentration of scutellarin. qRT-PCR further detected upregulated maternally expressed gene 3 (MEG3), oncogene c-Fos (c-FOS), and c-jun and downregulated M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase (PKM2), non-SMC Condensin I Complex Subunit H (NCAPH), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1, and TGF-α, suggesting that scutellarin with 300 μM volume inhibited the survival of SH-SY5Y by regulating the expression of these 8 factors. Scutellarin could be a novel drug for the treatment of neuroblastoma, and its underlying mechanism may be related to the upregulated levels of MEG3, c-FOS, and c-jun and downregulated the expression of PKM2, NCAPH, EGFR, TGF-β1, and TGF-α.
Keywords: HS‐SY5Y; neuroblastoma; proliferation inhibition; scutellarin.
© 2023 The Authors. Ibrain published by Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University and Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Role of estrogen receptor alpha in MEHP-induced proliferation and invasion of SH-SY5Y cells.Toxicology. 2021 Apr 15;453:152734. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2021.152734. Epub 2021 Feb 22. Toxicology. 2021. PMID: 33631300
-
Scutellarin Alleviates Ovalbumin-Induced Airway Remodeling in Mice and TGF-β-Induced Pro-fibrotic Phenotype in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells via MAPK and Smad2/3 Signaling Pathways.Inflammation. 2024 Jun;47(3):853-873. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01947-7. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 38168709 Free PMC article.
-
C18H17NO6 and Its Combination with Scutellarin Suppress the Proliferation and Induce the Apoptosis of Human Glioma Cells via Upregulation of Fas-Associated Factor 1 Expression.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Feb 20;2019:6821219. doi: 10.1155/2019/6821219. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30915356 Free PMC article.
-
Scutellarin-induced A549 cell apoptosis depends on activation of the transforming growth factor-β1/smad2/ROS/caspase-3 pathway.Open Life Sci. 2021 Sep 7;16(1):961-968. doi: 10.1515/biol-2021-0085. eCollection 2021. Open Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34568577 Free PMC article.
-
Scutellarin inhibits Hela cell growth and glycolysis by inhibiting the activity of pyruvate kinase M2.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017 Dec 15;27(24):5404-5408. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.11.011. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017. PMID: 29157862
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Role of Scutellarein in Neurological Disorders.Curr Pharm Des. 2025;31(20):1583-1592. doi: 10.2174/0113816128336901241125092132. Curr Pharm Des. 2025. PMID: 39781738 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
