Neutrophil-fibroblast crosstalk drives immunofibrosis in Crohn's disease through IFNα pathway
- PMID: 39346917
- PMCID: PMC11427415
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1447608
Neutrophil-fibroblast crosstalk drives immunofibrosis in Crohn's disease through IFNα pathway
Abstract
Introduction: Crohn's disease (CD) is characterized by chronic inflammation and intestinal fibrosis leading to lifelong complications. However, the disease pathogenesis remains elusive, and the therapeutic options are limited. Here, we investigated the interaction between neutrophils and intestinal fibroblasts in the development of CD immunofibrosis, a disease mechanism predisposing to inflammatory and fibrotic complications.
Methods: Peripheral neutrophils, enriched neutrophil extracellular traps (eNETs), serum, primary intestinal fibroblasts (PIFs) and intestinal biopsies from CD, ulcerative colitis (UC) patients, and healthy individuals (HI), were studied. Transcriptome analysis of neutrophils, multi-cytokine profiling and cell-based functional assays at mRNA/protein level were performed.
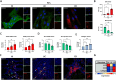
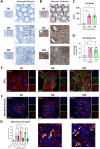
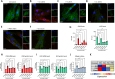
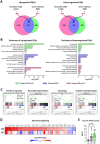
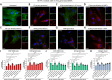
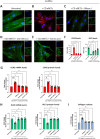
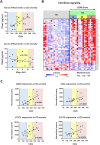
Results: Compared to UC, PIFs from CD patients, independently to the presence of strictures, displayed a distinct pro-fibrotic phenotype characterized by negative Krüppellike Factor-2 (KLF2) and increased cellular communication network factor-2 (CCN2) expression leading to collagen production. In both UC and CD, PIFs-derived IL-8 acted as a culprit chemoattractant for neutrophils in the intestine, where CD neutrophils were accumulated close to fibrotic lesions. Functionally, only CD neutrophils via eNETs induced a CD-like phenotype in HI PIFs, suggesting their fibrotic plasticity. High IFNa in serum and IFΝ-responsive signature in peripheral neutrophils were observed in CD, distinguishing it from UC. Moreover, CD serum stimulated the release of fibrogenic eNETs from neutrophils in an IFNa-dependent manner, suggesting the priming role of IFNa in circulating neutrophils. Inhibition of eNETs or JAK signaling in neutrophils or PIFs prevented the neutrophil-mediated fibrotic effect on PIFs. Furthermore, both serum IFNa levels and mRNA levels of key IFN signaling components in neutrophils were wellcorrelated with CD severity.
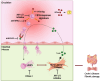
Conclusions: This study reveals the important role of the IFNa/neutrophil/fibroblast axis in CD immunofibrosis, suggesting candidate biomarkers and putative therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; IFNα; NETs; fibroblasts; immunofibrosis; neutrophils.
Copyright © 2024 Gavriilidis, Divolis, Natsi, Kafalis, Kogias, Antoniadou, Synolaki, Pavlos, Koutsi, Didaskalou, Papadimitriou, Tsironidou, Gavriil, Papadopoulos, Agelopoulos, Tsilingiris, Koffa, Giatromanolaki, Kouklakis, Ritis and Skendros.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

