Glycolysis-associated lncRNAs in cancer energy metabolism and immune microenvironment: a magic key
- PMID: 39346921
- PMCID: PMC11437524
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1456636
Glycolysis-associated lncRNAs in cancer energy metabolism and immune microenvironment: a magic key
Abstract
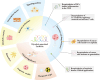
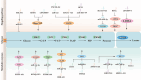
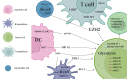
The dependence of tumor cells on glycolysis provides essential energy and raw materials for their survival and growth. Recent research findings have indicated that long chain non-coding RNAs (LncRNAs) have a key regulatory function in the tumor glycolytic pathway and offer new opportunities for cancer therapy. LncRNAs are analogous to a regulatory key during glycolysis. In this paper, we review the mechanisms of LncRNA in the tumor glycolytic pathway and their potential therapeutic strategies, including current alterations in cancer-related energy metabolism with lncRNA mediating the expression of key enzymes, lactate production and transport, and the mechanism of interaction with transcription factors, miRNAs, and other molecules. Studies targeting LncRNA-regulated tumor glycolytic pathways also offer the possibility of developing new therapeutic strategies. By regulating LncRNA expression, the metabolic pathways of tumor cells can be interfered with to inhibit tumor growth and metastasis, thus affecting the immune and drug resistance mechanisms of tumor cells. In addition, lncRNAs have the capacity to function as molecular markers and target therapies, thereby contributing novel strategies and approaches to the field of personalized cancer therapy and prognosis evaluation. In conclusion, LncRNA, as key molecules regulating the tumor glycolysis pathway, reveals a new mechanism of abnormal metabolism in cancer cells. Future research will more thoroughly investigate the specific mechanisms of LncRNA glycolysis regulation and develop corresponding therapeutic strategies, thereby fostering new optimism for the realization of precision medicine.
Keywords: cancer; glycolysis; immune; lncRNA; metabolism.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Zhang, Liu, Zeng and Song.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

