Evaluating Soil-Vegetable Contamination with Heavy Metals in Bogura, Bangladesh: A Risk Assessment Approach
- PMID: 39346962
- PMCID: PMC11437587
- DOI: 10.1177/11786302241282601
Evaluating Soil-Vegetable Contamination with Heavy Metals in Bogura, Bangladesh: A Risk Assessment Approach
Abstract
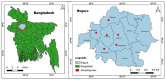
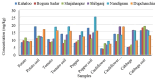
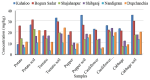
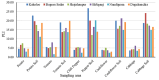
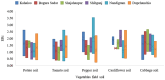
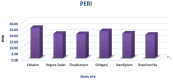
This study quantified hazardous heavy metals (Cu, Cr, and Pb) in soil and vegetables (potato, tomato, pepper, cauliflower, and cabbage) across six upazilas (Kahaloo, Bogura Sadar, Shajahanpur, Shibganj, Nandigram, and Dupchanchia) in Bogura district, Bangladesh, assessing their health and environmental impacts. The detection method was validated for its accuracy and precision with QC samples. Results indicated that Cu levels in all samples were within safe limits set by BFSA and FAO/WHO, whereas Cr and Pb in vegetables exceeded permissible levels, though soil concentrations remained within limits. Pb contamination was particularly severe in vegetables (CF > 6), and all vegetables showed significant contamination degrees (CD), highlighting extensive heavy metal pollution. The Pollution Load Index (PLI) identified Kahaloo and Bogura Sadar as the most polluted, whereas Nandigram and Dupchanchia were the least. Bioaccumulation factors (BF) for all metals were <1, suggesting minimal transfer to edible parts. However, the ecological risk index (ERi) and potential ecological risk index (PERI) suggested low ecological risks, but health risk assessments indicated that vegetable consumption poses significant carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risks (CHR > 10-4, HI > 1) across all upazilas. The findings underscore the urgent need for measures to mitigate heavy metal pollution in these areas to safeguard environmental and public health.
Keywords: Bogura; Vegetables; environmental pollution; heavy metals; risk assessment; soil.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Khan S, Cao Q, Zheng YM, Huang YZ, Zhu YG. Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China. Environ Pollut. 2008;152:686-692. - PubMed
-
- Muchuweti M, Birkett JW, Chinyanga E, et al. Heavy metal content of vegetables irrigated with mixtures of wastewater and sewage sludge in Zimbabwe: implications for human health. Agric Ecosyst Environ. 2006;112:41-48.
-
- Alloway BJ. Sources of heavy metals and metalloids in soils. In: Alloway BJ, ed. Heavy Metals in Soils: Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and Their Bioavailability. Springer; 2013:11-50.
-
- Nagajyoti PC, Lee KD, Sreekanth TVM. Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett. 2010;8:199-216.
-
- Guo W, Liu X, Liu Z, Li G. Pollution and potential ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in the sediments around Dongjiang Harbor, Tianjin. Procedia Environ Sci. 2010;2:729-736.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

