Emodin Attenuates the ECM Degradation and Oxidative Stress of Chondrocytes through the Nrf2/NQO1/HO-1 Pathway to Ameliorate Rat Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 39346968
- PMCID: PMC11427723
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5581346
Emodin Attenuates the ECM Degradation and Oxidative Stress of Chondrocytes through the Nrf2/NQO1/HO-1 Pathway to Ameliorate Rat Osteoarthritis
Abstract
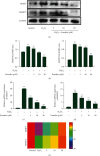
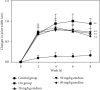
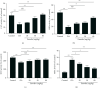
Osteoarthritis (OA) substantially reduces the quality of life of the elderly. OA therapy remains a challenge since no treatment options for its causes are so far available. Over recent years, researchers have speculated that emodin may represent a potential treatment strategy for OA. However, it remains unclear whether the mechanism of action of emodin is associated with the inhibition of OA-induced oxidative stress. In the present study, the potential antioxidant mechanism of action of emodin and its protective properties against the development of OA were investigated both in vitro and in vivo. In vitro, emodin inhibited the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in chondrocytes induced by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and reduced the expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)3 and MMP13 in a concentration-dependent manner. It was found that emodin upregulated the Nrf2/NQO1/HO-1 pathway, thereby attenuating the effects of oxidative stress caused by OA. In a rat model of posttraumatic OA induced by anterior cruciate ligament transection (ACLT), emodin reduced the extent of joint swelling. Emodin attenuated oxidative damage in the cartilage by upregulating superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione (GSH) activity, reducing malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration and inhibiting the expression of the extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation biomarkers cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP), and C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (CTX-I) and type II collagen (CTX-II), thereby reducing cartilage damage. In summary, the present study indicates that emodin reduces ECM degradation and oxidative stress in chondrocytes via the Nrf2/NQO1/HO-1 pathway, thereby ameliorating OA in rats.
Copyright © 2022 Tianwen Ma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Ginkgolide C slows the progression of osteoarthritis by activating Nrf2/HO-1 and blocking the NF-κB pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 28;13:1027553. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1027553. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36386227 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin Modulates Ferroptosis via the SIRT1/Nrf-2/HO-1 Pathway and Attenuates Cartilage Destruction in an Osteoarthritis Rat Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 7;25(13):7461. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137461. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000568 Free PMC article.
-
Emodin ameliorates cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis by inhibiting NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin signaling in-vitro and in-vivo.Int Immunopharmacol. 2018 Aug;61:222-230. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.05.026. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29890416
-
Bardoxolone-Methyl Prevents Oxidative Stress-Mediated Apoptosis and Extracellular Matrix Degradation in vitro and Alleviates Osteoarthritis in vivo.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Sep 4;15:3735-3747. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S314767. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 34511883 Free PMC article.
-
Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein, C-terminal cross-linking telopeptide of type II collagen, and matrix metalloproteinase-3 as biomarkers for knee and hip osteoarthritis (OA) diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 May;27(5):726-736. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2018.10.009. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019. PMID: 30391538
Cited by
-
Emodin alleviates the damage to lens epithelial cells in diabetic cataract by repressing the p53-mediated ferroptosis pathway.Int Ophthalmol. 2025 Apr 2;45(1):141. doi: 10.1007/s10792-025-03513-6. Int Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40175804
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

