Polarization-resolved analysis of outer retinal bands: investigating ballistic and multiply scattered photons using full-field swept-source optical coherence tomography
- PMID: 39346986
- PMCID: PMC11427207
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.523202
Polarization-resolved analysis of outer retinal bands: investigating ballistic and multiply scattered photons using full-field swept-source optical coherence tomography
Abstract
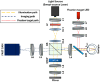
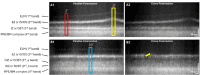
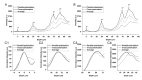
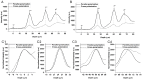
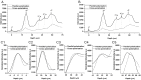
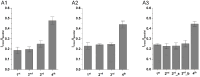
Precise interpretation of the anatomical origins of outer retinal optical coherence tomography (OCT) presents technical challenges owing to the delicate nature of the retina. To address this challenge, our study introduces a novel polarization-sensitive full-field swept-source OCT (FF-SS-OCT) that provides parallel-polarization and cross-polarization OCT measurements, predominantly capturing ballistically reflected photons and multiply scattered photons, respectively. Notably, parallel-polarization OCT unveils layer-like structures more effectively, including the inner plexiform layer (IPL) sub-layers, outer plexiform layer (OPL) sub-layers (in rod-dominant regions), and rod/cone outer segment (OS) tips, compared to cross-polarization OCT, where such sub-layers are not visible. Through a comparative analysis of parallel-polarization and cross-polarization OCT images of the outer retina, we discovered that the 2nd outer retinal OCT band results from contributions from both the ellipsoid zone (EZ) and the inner segment/outer segment (IS/OS) junction. Similarly, the 3rd outer retinal OCT band appears to reflect contributions from both the interdigitation zone (IZ) and photoreceptor OS tips. This polarization-sensitive approach advances our understanding of the origins of outer retinal OCT signals and proposes potential new biomarkers for assessing retinal health and diseases.
© 2024 Optica Publishing Group.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest related to this article.
Figures

Update of
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
