In vivo bioluminescence tomography-guided system for pancreatic cancer radiotherapy research
- PMID: 39347008
- PMCID: PMC11427198
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.523916
In vivo bioluminescence tomography-guided system for pancreatic cancer radiotherapy research
Abstract
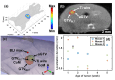
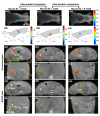
Recent development of radiotherapy (RT) has heightened the use of radiation in managing pancreatic cancer. Thus, there is a need to investigate pancreatic cancer in a pre-clinical setting to advance our understanding of the role of RT. Widely-used cone-beam CT (CBCT) imaging cannot provide sufficient soft tissue contrast to guide irradiation. The pancreas is also prone to motion. Large collimation is unavoidably used for irradiation, costing normal tissue toxicity. We innovated a bioluminescence tomography (BLT)-guided system to address these needs. We established an orthotopic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) mouse model to access BLT. Mice underwent multi-projection and multi-spectral bioluminescence imaging (BLI), followed by CBCT imaging in an animal irradiator for BLT reconstruction and radiation planning. With optimized absorption coefficients, BLT localized PDAC at 1.25 ± 0.19 mm accuracy. To account for BLT localization uncertainties, we expanded the BLT-reconstructed volume with margin to form planning target volume(PTVBLT) for radiation planning, covering 98.7 ± 2.2% of PDAC. The BLT-guided conformal plan can cover 100% of tumors with limited normal tissue involvement across both inter-animal and inter-fraction cases, superior to the 2D BLI-guided conventional plan. BLT offers unique opportunities to localize PDAC for conformal irradiation, minimize normal tissue involvement, and support reproducibility in RT studies.
© 2024 Optica Publishing Group.
Conflict of interest statement
The research group of Dr. Ken Kang-Hsin Wang and Xstrahl are supported by NIH academic-industrial partnership R37CA230341 in the development of BLT-guided system for pre-clinical radiation research.
Figures




References
-
- . “Chemoimmunotherapy and radiation in pancreatic cancer (CRIT),” (ClinicalTrials.gov.).
-
- . “Pancreatic tumor cell vaccine (GVAX), low dose cyclophosphamide, fractionated stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT), and folfirinox chemotherapy in patients with resected adenocarcinoma of the pancreas,” (ClinicalTrials.gov.).
-
- . “Immune checkpoint inhibition (Tremelimumab and/or MEDI4736) in combination with radiation therapy in patients with unresectable pancreatic cancer,” (ClinicalTrials.gov.).
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
