Injectable decellularized Wharton's jelly hydrogel containing CD56+ umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for meniscus tear healing and cartilage protection
- PMID: 39347017
- PMCID: PMC11437876
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101258
Injectable decellularized Wharton's jelly hydrogel containing CD56+ umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for meniscus tear healing and cartilage protection
Abstract
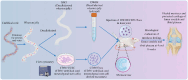
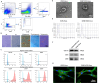
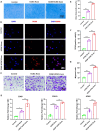
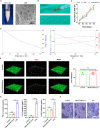
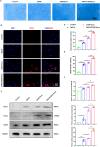
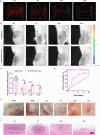
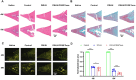
Traditional meniscectomy or suture for meniscal tear usually leads to failed self-healing, cartilage degeneration and worse osteoarthritis. The strategies that facilitate the healing process of torn meniscus and safeguard knee cartilage against degeneration will be promising for clinical therapy. The CD56+ umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (UCSCs) (CD56+UCSCs) were sorted from Wharton's jelly using flow cytometer. Then, the modified decellularized Wharton's Jelly hydrogel (DWJH) was combined with isolated CD56+Exos from CD56+UCSCs to fabricate DWJH/CD56+Exos. The in vitro studies were performed to characterize the DWJ (decellularized Wharton's Jelly). The injectability and rheological properties were assessed by shear rate and frequency sweep analysis. The biocompatibility and chondrogenic differentiation inducibility of DWJH/CD56+Exos were performed on human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (hBMSCs) and RAW 264.7 cells. The release dynamics was evaluated in vitro and in vivo experiments. As for the in vivo experiments, the operated rats that subjected to a 2 mm full-thickness longitudinal tear in right medial anterior meniscus were injected a single dose of DWJH/CD56+Exos. At 4 and 8 weeks postoperatively, torn meniscus healing and articular cartilage degeneration were evaluated by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), safranin O/fast green (SO&FG), and Sirius red staining. In in vitro experiments, the injectable DWJH/CD56+Exos demonstrated excellent biocompatibility, exosome releasing efficiency, injectable property and chondrogenic inducibility. The results of in vivo experiments revealed that DWJH/CD56+Exos degraded over time, promoted meniscal chondrogenesis, organized meniscal extracellular matrix remodeling, safeguard articular cartilage and inhibited secondary cartilage degeneration, which accelerated further facilitated torn meniscus healing. The novel injectable DWJH/CD56+Exos promoted meniscal tear healing by promoting meniscal chondrogenesis, safeguarding articular cartilage, and inhibiting secondary cartilage degeneration.
Keywords: CD56; Decellularized Wharton's jelly hydrogel; Exosome; Meniscal tear; Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Englund M., Roemer F.W., Hayashi D., Crema M.D., Guermazi A. Meniscus pathology, osteoarthritis and the treatment controversy. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012;8(7):412–419. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto S., Ichinose T., Ohsawa T., Koibuchi N., Chikuda H. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy accelerates the healing of a meniscal tear in the avascular region in a rat model. Am. J. Sports Med. 2019;47(12):2937–2944. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

