Polyethylene wear and cup migration of cemented total hip arthroplasty with femoral heads made of oxidized zirconium, steel, or cobalt chromium: a 10-year secondary analysis from a randomized trial using radiostereometry
- PMID: 39347798
- PMCID: PMC11441331
- DOI: 10.2340/17453674.2024.41945
Polyethylene wear and cup migration of cemented total hip arthroplasty with femoral heads made of oxidized zirconium, steel, or cobalt chromium: a 10-year secondary analysis from a randomized trial using radiostereometry
Abstract
Background and purpose: We aimed to evaluate polyethylene (PE) wear, cup migration, and clinical outcome over 10 years in total hip arthroplasties (THA) using different articulations.
Methods: This is a secondary analysis of 150 patients randomized into 5 groups, using different articulations: Charnley/Charnley Ogee for steel and conventional polyethylene (CPE), or Spectron EF/Reflection with either CPE or highly cross linked polyethylene (XLPE) cups, paired with heads made of either cobalt-chromium (CoCr) or oxidized zirconium (OxZr). All cups were cemented. Patients underwent repeated radiostereometric analysis (RSA) measurements for up to 10 years to assess wear and migration. Clinical outcome was assessed using Harris Hip Score (HHS).
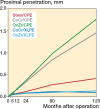
Results: After 10 years, the XLPE cups demonstrated low wear rates: 0.08 mm (95% confidence interval [CI] -0.11 to 0.26 mm) with CoCr heads and 0.06 mm (CI -0.14 to 0.26 mm) with OxZr heads, with a mean difference of 0.01 mm (CI -0.26 to 0.29 mm). In contrast, CPE cups exhibited significantly more wear: 1.35 mm (CI 1.16 to 1.55 mm) with CoCr heads and 1.68 mm (CI 1.44 to 1.92 mm) with OxZr heads, with a mean difference of 0.33 mm (CI 0.02 to 0.64 mm). The Charnley/Ogee group (CPE) showed PE wear of 0.34 mm (CI 0.12 to 0.56 mm). The CPE groups with OxZr and CoCr heads had 0.67 mm (CI 0.38 to 0.96 mm) and 0.35 mm (CI 0.09 to 0.61 mm) greater proximal migration respectively than the corresponding XLPE groups. HHS was similar across all groups.
Conclusion: We found no significant advantage of OxZr over CoCr heads in reducing wear or migration. XLPE demonstrated a major reduction in wear as well as a reduction in cup migration compared with CPE. Charnley performed better than the other CPE cups in terms of PE wear and cup migration. No differences in clinical outcome were found.
Figures


References
-
- McKellop H, Shen F W, Lu B, Campbell P, Salovey R. Effect of sterilization method and other modifications on the wear resistance of acetabular cups made of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene: a hip-simulator study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2000; 82(12): 1708-25. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200012000-00004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Muratoglu O K, Bragdon C R, O’Connor D O, Jasty M, Harris W H. A novel method of cross-linking ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene to improve wear, reduce oxidation, and retain mechanical properties. Recipient of the 1999 HAP Paul Award. J Arthroplasty 2001; 16(2): 149-60. doi: 10.1054/arth.2001.20540. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

