Bilateral purtscher-like retinopathy associated with DRESS syndrome: a case report
- PMID: 39347877
- PMCID: PMC11442731
- DOI: 10.1186/s12348-024-00433-x
Bilateral purtscher-like retinopathy associated with DRESS syndrome: a case report
Abstract
Background: To report a case of Bilateral Purtscher-like retinopathy associated with DRESS syndrome managed with ocular and systemic treatments.
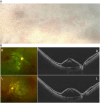
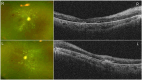
Case presentation: A 29-year-old healthy female developed multi-organ (cutaneous, hematologic, renal and hepatic) disfunction and profound vision loss 1 month after Human papillomavirus vaccine injection. At the first presentation, her visual acuity was counting fingers in both eyes. Fundus exam showed remarkable cotton-wool spots, retinal hemorrhages and macular edema. She was diagnosed DRESS syndrome and Purtscher-like retinopathy and treated with intravitreal injection of ranibizumab, systemic steroids anticoagulants, and plasma exchange. The patient finally recovered from this life-threatening condition but left with permanent visual damage.
Conclusion: Purtscher-like retinopathy could be complicated by DRESS syndrome which is usually considered a type IV hypersensitivity reaction.
Keywords: DRESS syndrome; Delayed hypersensitivity reaction; Inflammatory storm; Purtscher-like retinopathy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kardaun SH, Sekula P, Valeyrie-Allanore L, Liss Y, Chu CY, Creamer D, Sidoroff A, Naldi L, Mockenhaupt M, Roujeau JC, RegiSCAR study group (2013) & Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): an original multisystem adverse drug reaction. Results from the prospective RegiSCAR study. Br J Dermatol, 2013. 169(5): pp. 1071-80 - PubMed
-
- Thatcher MD, Wu LZ, Varma R (2023) Bilateral Purtscher-Like Retinopathy Associated With COVID-19 Infection. JAMA Ophthalmol, 2023. 141(3): pp. 291–293 - PubMed
-
- Agrawal A, McKibbin MA (2006) Purtscher’s and Purtscher-like retinopathies: a review. Surv Ophthalmol, 2006. 51(2): pp. 129 – 36 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources