Insulin-inspired hippocampal neuron-targeting technology for protein drug delivery
- PMID: 39348543
- PMCID: PMC11474037
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2407936121
Insulin-inspired hippocampal neuron-targeting technology for protein drug delivery
Abstract
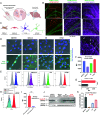
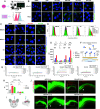
Hippocampal neurons can be the first to be impaired with neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer's disease (AD). Most drug candidates for causal therapy of AD cannot either enter the brain or accumulate around hippocampal neurons. Here, we genetically engineered insulin-fusion proteins, called hippocampal neuron-targeting (Ht) proteins, for targeting protein drugs to hippocampal neurons because insulin tends to accumulate in the neuronal cell layers of the hippocampus. In vitro examinations clarified that insulin and Ht proteins were internalized into the cultured hippocampal neurons through insulin receptor-mediated macropinocytosis. Cysteines were key determinants of the delivery of Ht proteins to hippocampal neurons, and insulin B chain mutant was most potent in delivering cargo proteins. In vivo accumulation of Ht proteins to hippocampal neuronal layers occurred after intracerebroventricular administration. Thus, hippocampal neuron-targeting technology can provide great help for developing protein drugs against neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; drug delivery; fusion protein; hippocampal neuron; insulin.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures




Comment in
-
Insulin-inspired peptides may open new pathways to treat Alzheimer's disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Dec 3;121(49):e2419741121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2419741121. Epub 2024 Nov 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39585998 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
CTBP1 Confers Protection for Hippocampal and Cortical Neurons in Rat Models of Alzheimer's Disease.Neuroimmunomodulation. 2019;26(3):139-152. doi: 10.1159/000500942. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2019. PMID: 31340205
-
Insulin-like growth factor 1 gene transfer for sporadic Alzheimer's disease: New evidence for trophic factor mediated hippocampal neuronal and synaptic recovery-based behavior improvement.Hippocampus. 2021 Oct;31(10):1137-1153. doi: 10.1002/hipo.23379. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Hippocampus. 2021. PMID: 34324234
-
An anti-diabetes agent protects the mouse brain from defective insulin signaling caused by Alzheimer's disease- associated Aβ oligomers.J Clin Invest. 2012 Apr;122(4):1339-53. doi: 10.1172/JCI57256. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 22476196 Free PMC article.
-
The role of neuronal insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease: possible therapeutic implications.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2014 Mar;13(2):322-37. doi: 10.2174/18715273113126660141. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2014. PMID: 24059318 Review.
-
Reengineering biopharmaceuticals for targeted delivery across the blood-brain barrier.Methods Enzymol. 2012;503:269-92. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-396962-0.00011-2. Methods Enzymol. 2012. PMID: 22230573 Review.
Cited by
-
Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier: Innovations in Receptor- and Transporter-Mediated Transcytosis Strategies.Pharmaceutics. 2025 May 28;17(6):706. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17060706. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40574019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in brain-targeted delivery strategies and natural product-mediated enhancement of blood-brain barrier permeability.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 May 26;23(1):382. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03415-w. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40420216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin-inspired peptides may open new pathways to treat Alzheimer's disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Dec 3;121(49):e2419741121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2419741121. Epub 2024 Nov 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39585998 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- van Dyck C. H., et al. , Lecanemab in early Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 388, 9–21 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

