Metabolic resistance of Aβ3pE-42, a target epitope of the anti-Alzheimer therapeutic antibody, donanemab
- PMID: 39348937
- PMCID: PMC11443169
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202402650
Metabolic resistance of Aβ3pE-42, a target epitope of the anti-Alzheimer therapeutic antibody, donanemab
Abstract
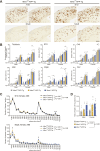
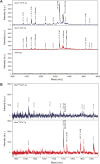
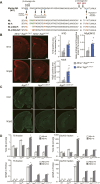
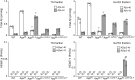
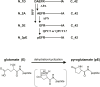
The amyloid β peptide (Aβ), starting with pyroglutamate (pE) at position 3 and ending at position 42 (Aβ3pE-42), predominantly accumulates in the brains of Alzheimer's disease. Consistently, donanemab, a therapeutic antibody raised against Aβ3pE-42, has been shown to be effective in recent clinical trials. Although the primary Aβ produced physiologically is Aβ1-40/42, an explanation for how and why this physiological Aβ is converted to the pathological form remains elusive. Here, we present experimental evidence that accounts for the aging-associated Aβ3pE-42 deposition: Aβ3pE-42 was metabolically more stable than other Aβx-42 variants; deficiency of neprilysin, the major Aβ-degrading enzyme, induced a relatively selective deposition of Aβ3pE-42 in both APP transgenic and App knock-in mouse brains; Aβ3pE-42 deposition always colocalized with Pittsburgh compound B-positive cored plaques in APP transgenic mouse brains; and under aberrant conditions, such as a significant reduction in neprilysin activity, aminopeptidases, dipeptidyl peptidases, and glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase-like were up-regulated in the progression of aging, and a proportion of Aβ1-42 may be processed to Aβ3pE-42. Our findings suggest that anti-Aβ therapies are more effective if given before Aβ3pE-42 deposition.
© 2024 Iwata et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures












References
-
- Antonyan A, Schlenzig D, Schilling S, Naumann M, Sharoyan S, Mardanyan S, Demuth HU (2018) Concerted action of dipeptidyl peptidase IV and glutaminyl cyclase results in formation of pyroglutamate-modified amyloid peptides in vitro. Neurochem Int 113: 112–119. 10.1016/j.neuint.2017.12.001 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
