BMP Antagonist Gremlin 2 Regulates Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Is Associated with Seizure Susceptibility and Anxiety
- PMID: 39349059
- PMCID: PMC11493175
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0213-23.2024
BMP Antagonist Gremlin 2 Regulates Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Is Associated with Seizure Susceptibility and Anxiety
Abstract
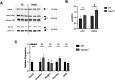
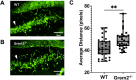
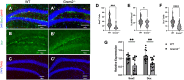
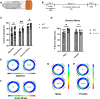
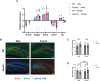
The Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) signaling pathway is vital in neural progenitor cell proliferation, specification, and differentiation. The BMP signaling antagonist Gremlin 2 (Grem2) is the most potent natural inhibitor of BMP expressed in the adult brain; however its function remains unknown. To address this knowledge gap, we have analyzed mice lacking Grem2 via homologous recombination (Grem2-/- ). Histological analysis of brain sections revealed significant scattering of CA3 pyramidal cells within the dentate hilus in the hippocampus of Grem2-/- mice. Furthermore, the number of proliferating neural stem cells and neuroblasts was significantly decreased in the subgranular zone of Grem2-/- mice compared with that of wild-type (WT) controls. Due to the role of hippocampal neurogenesis in neurological disorders, we tested mice on a battery of neurobehavioral tests. Grem2-/- mice exhibited increased anxiety on the elevated zero maze in response to acute and chronic stress. Specifically, male Grem2-/- mice showed increased anxiogenesis following chronic stress, and this was correlated with higher levels of BMP signaling and decreased proliferation in the dentate gyrus. Additionally, when chemically challenged with kainic acid, Grem2-/- mice displayed a higher susceptibility to and increased severity of seizures compared with WTs. Together, our data indicate that Grem2 regulates BMP signaling and is vital in maintaining homeostasis in adult hippocampal neurogenesis and structure. Furthermore, the lack of Grem2 contributes to the development and progression of neurogenesis-related disorders such as anxiety and epilepsy.
Keywords: BMP signaling; Gremlin 2; anxiety; epilepsy; hippocampal neurogenesis.
Copyright © 2024 Frazer et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
