Effect of high-dose N-acetylcysteine on exacerbations and lung function in patients with mild-to-moderate COPD: a double-blind, parallel group, multicentre randomised clinical trial
- PMID: 39349461
- PMCID: PMC11442465
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-51079-1
Effect of high-dose N-acetylcysteine on exacerbations and lung function in patients with mild-to-moderate COPD: a double-blind, parallel group, multicentre randomised clinical trial
Abstract
Evidence for the treatment of patients with mild-to-moderate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is limited. The efficacy of N-acetylcysteine (an antioxidant and mucolytic agent) for patients with mild-to-moderate COPD is uncertain. In this multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, we randomly assigned 968 patients with mild-to-moderate COPD to treatment with N-acetylcysteine (600 mg, twice daily) or matched placebo for two years. Eligible participants were 40-80 years of age and had mild-to-moderate COPD (forced expiratory volume in 1 second [FEV1] to forced vital capacity ratio <0.70 and an FEV1 ≥ 50% predicted value after bronchodilator use). The coprimary outcomes were the annual rate of total exacerbations and the between-group difference in the change from baseline to 24 months in FEV1 before bronchodilator use. COPD exacerbation was defined as the appearance or worsening of at least two major symptoms (cough, expectoration, purulent sputum, wheezing, or dyspnoea) persisting for at least 48 hours. Assessment of exacerbations was conducted every three months, and lung function was performed annually after enrolment. The difference between the N-acetylcysteine group and the placebo group in the annual rate of total exacerbation were not significant (0.65 vs. 0.72 per patient-year; relative risk [RR], 0.90; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.80-1.02; P = 0.10). There was no significant difference in FEV1 before bronchodilator use at 24 months. Long-term treatment with high-dose N-acetylcysteine neither significantly reduced the annual rate of total exacerbations nor improved lung function in patients with mild-to-moderate COPD. Chinese Clinical Trial Registration: ChiCTR-IIR-17012604.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare: no support from any organization for the submitted work; no financial relationships with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous three years; no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
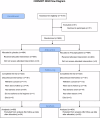
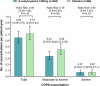

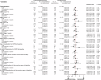
References
-
- Zhong, N. et al. Prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in China: a large, population-based survey. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med.176, 753–760 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Wang, C. et al. Prevalence and risk factors of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in China (the China Pulmonary Health [CPH] study): a national cross-sectional study. Lancet391, 1706–1717 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

