Sensitive infant care tunes a frontotemporal interbrain network in adolescence
- PMID: 39349700
- PMCID: PMC11442694
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-73630-2
Sensitive infant care tunes a frontotemporal interbrain network in adolescence
Abstract
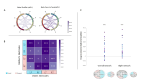
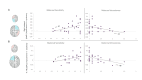
Caregiving plays a critical role in children's cognitive, emotional, and psychological well-being. In the current longitudinal study, we investigated the enduring effects of early maternal behavior on processes of interbrain synchrony in adolescence. Mother-infant naturalistic interactions were filmed when infants were 3-4 months old and interactions were coded for maternal sensitivity and intrusiveness with the Coding Interactive Behavior Manual. In early adolescence (Mean = 12.30, SD = 1.25), mother-adolescent interbrain synchrony was measured using hyperscanning EEG during a naturalistic interaction of positive valence. Guided by previous hyperscanning studies, we focused on interbrain connections within the right frontotemporal interbrain network. Results indicate that maternal sensitivity in early infancy was longitudinally associated with neural synchrony in the right interbrain frontotemporal network. Post-hoc comparisons highlighted enhancement of mother-adolescent frontal-frontal connectivity, a connection that has been implicated in parent-child social communication. In contrast, maternal intrusiveness in infancy was linked with attenuation of interbrain synchrony in the right interbrain frontotemporal network. Sensitivity and intrusiveness are key maternal social orientations that have shown to be individually stable in the mother-child relationship from infancy to adulthood and foreshadow children's positive and negative social-emotional outcomes, respectively. Our findings are the first to demonstrate that these two maternal orientations play a role in enhancing or attenuating the child's interbrain frontotemporal network, which sustains social communication and affiliation. Results suggest that the reported long-term impact of maternal sensitivity and intrusiveness may relate, in part, to its effects on tuning the child's brain to sociality.
Keywords: EEG; Hyperscanning; Maternal sensitivity; Mother-child relationships; Social development; Social neuroscience; Synchrony.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Van Der Voort, A., Juffer, F. & Bakermans-Kranenburg, J. Sensitive parenting is the foundation for secure attachment relationships and positive social-emotional development of children. J. Child. Serv.9, 165–176 (2014). - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

