Aspartyl proteases target host actin nucleator complex protein to limit epithelial innate immunity
- PMID: 39349750
- PMCID: PMC11549443
- DOI: 10.1038/s44319-024-00270-y
Aspartyl proteases target host actin nucleator complex protein to limit epithelial innate immunity
Abstract
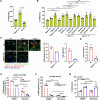
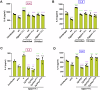
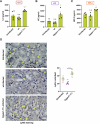
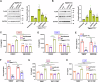
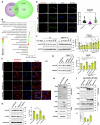
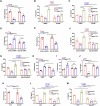
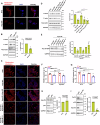
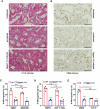
Epithelial-immune cell communication is pivotal to control microbial infections. We show that glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked aspartyl proteases (Yapsins) of the human opportunistic pathogenic yeast Candida glabrata (Cg) thwart epithelial cell (EC)-neutrophil signalling by targeting the EC protein, Arpc1B (actin nucleator Arp2/3 complex subunit), which leads to actin disassembly and impeded IL-8 secretion by ECs. Further, the diminished IL-8 secretion inhibits neutrophil migration, and protects Cg from the neutrophil-mediated killing. CgYapsin-dependent Arpc1B degradation requires Arginine-142 in Arpc1B, and leads to reduced Arpc1B-p38 MAPK interaction and downregulated p38 signalling. Consistently, Arpc1B or p38 deletion promotes survival of the Cg aspartyl protease-deficient mutant in ECs. Importantly, kidneys of the protease-deficient mutant-infected mice display elevated immune cell infiltration and cytokine secretion, implicating CgYapsins in immune response suppression in vivo. Besides delineating Cg-EC interplay, our results uncover a novel target, Arpc1B, that pathogens attack to constrain the host signalling networks, and link Arpc1B mechanistically with p38 activation.
Keywords: Candida glabrata; Arp2/3 Complex; Epa1 Adhesin; Epithelial Cells; p38 MAPK.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Abella JVG, Galloni C, Pernier J, Barry DJ, Kjær S, Carlier MF, Way M (2016) Isoform diversity in the Arp2/3 complex determines actin filament dynamics. Nat Cell Biol 18:76–86 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

