LncRNA MIAT suppresses inflammation in LPS-induced J774A.1 macrophages by promoting autophagy through miR-30a-5p/SOCS1 axi
- PMID: 39349964
- PMCID: PMC11442610
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-73607-1
LncRNA MIAT suppresses inflammation in LPS-induced J774A.1 macrophages by promoting autophagy through miR-30a-5p/SOCS1 axi
Abstract
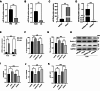
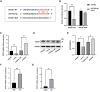
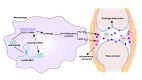
Accumulated data implicate that long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) plays a pivotal role in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), potentially serving as a competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) for microRNAs (miRNAs). The lncRNA myocardial infarction-associated transcript (MIAT) has been demonstrated to regulate inflammation. However, the role of MIAT in the inflammation of RA remains inadequately explored. This study aims to elucidate MIAT's role in the inflammation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced macrophages and to uncover the underlying molecular mechanisms. We observed heightened MIAT expression in LPS-induced J774A.1 cells and collagen-induced arthritis mouse models, in contrast to the expression pattern of miR-30a-5p. Silencing MIAT resulted in increased expression of the inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNF-α. Simultaneously, MIAT interference significantly impeded macrophage autophagy, evidenced by decreased expression of autophagy-related markers LC3-II and Beclin-1, alongside increased levels of p62 in LPS-induced J774A.1 cells. Notably, MIAT functioned as a ceRNA, sponging miR-30a-5p and exerting a negative regulatory influence on its expression. SOCS1 emerged as a target of miR-30a-5p, modulated by MIAT. Mechanistically, inhibiting miR-30a-5p reversed the impact of MIAT deficiency in promoting LPS-induced inflammation, while SOCS1 knockdown countered the cytokine inhibitory effect induced by silencing miR-30a-5p. In summary, this study indicates that lncRNA MIAT suppresses inflammation in LPS-induced J774A.1 macrophages by stimulating autophagy through the miR-30a-5p/SOCS1 axis. This suggests that MIAT holds promise as a potential therapeutic target for RA inflammation.
Keywords: Autophagy; Inflammation; LncRNA MIAT; Rheumatoid arthritis; miR-30a-5p/SOCS1 axis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

