Undergraduate dental sleep medicine teaching at German university dental schools - a questionnaire-based survey
- PMID: 39350224
- PMCID: PMC11443930
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-024-06042-5
Undergraduate dental sleep medicine teaching at German university dental schools - a questionnaire-based survey
Abstract
Purpose: Diagnosing and treating obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) requires fundamental understanding of sleep medicine, including training and clinical experience. So far, dental sleep medicine (DSM) has not yet become a mandatory part of dental education in Germany. This questionnaire-based survey for both lecturers and students aimed to evaluate DSM education among undergraduate students.
Methods: A structured questionnaire was sent to the managing directors and student councils of all 30 German university dental schools. The questionnaire contained 13 questions on teaching quantity and content, lecturers' knowledge, and future interest in DSM. For each university dental school, only one questionnaire should be completed by the student council and the managing director. A scoring system assessed lecturers' knowledge based on clinical experience and qualifications. Descriptive data and correlation coefficients were calculated (P < 0.05).
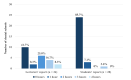
Results: The responses of 24 lecturers (80%) and 28 students (93.3%) could be evaluated. DSM was reported to be included in the curriculum by 14 lecturers (58.3%) and 4 students (14.3%). Mean teaching hours per semester were 1.4 ± 1.4 h (lecturers) and 0.2 ± 0.6 h (students) accordingly. Greater knowledge of lecturers in DSM was positively correlated with the inclusion of DSM in the curriculum (P = 0.022) and with the number of teaching hours per semester (P = 0.001).
Conclusion: Postgraduate education and incorporating DSM knowledge into undergraduate education ("Teach the Teacher") seems to play a key role in fundamentally training future dentists in this field.
Keywords: Dental curriculum; Dental education; Dental sleep medicine; Sleep medicine; Undergraduate student.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Narang I, McCrindle BW, Manlhiot C, et al. Intermittent nocturnal hypoxia and metabolic risk in obese adolescents with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath. 2018;22:1037–44. 10.1007/s11325-018-1631-9. - PubMed
-
- Behrents RG, Shelgikar AV, Conley RS, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea and orthodontics: an American Association of Orthodontists White Paper. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2019;156:13–e281. 10.1016/j.ajodo.2019.04.009. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources