Pre-clinical evaluation and optimization of image quality for a Next Generation Tomosynthesis prototype
- PMID: 39351015
- PMCID: PMC11441092
- DOI: 10.1117/12.2608811
Pre-clinical evaluation and optimization of image quality for a Next Generation Tomosynthesis prototype
Abstract
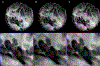
A next generation tomosynthesis (NGT) prototype has been developed to investigate alternative scanning geometries for digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT). The NGT system uses a 2D plane as an address space for the x-ray source to define an acquisition geometry. In previous work, tests of physics have been used as objective metrics to evaluate image quality for NGT. In this work, the performance of custom NGT acquisition geometries is evaluated for mastectomy specimens to validate previous phantom experiments. Two custom acquisition geometries - incorporating T- and K-shaped source motion paths in the posteroanterior direction - were compared with a conventional DBT acquisition geometry. Noise power spectra (NPS) are calculated using 3D image reconstructions of the three acquisition geometries to evaluate the degradation of image quality due to noise and to visualize NGT sampling properties in the Fourier domain. NPS are used to describe features of the specimen image reconstructions and compare acquisition geometries. NGT acquisition geometries were found to improve high-frequency performance with isotropic super resolution, reduce out-of-plane reconstruction artifacts, and improve overall image reconstruction quality. The T-geometry combines the benefits of narrow- and wide-angle tomosynthesis in a single scan improving high-frequency spatial resolution and out-of-plane blurring, respectively.
Keywords: acquisition geometry; cone beam artifact; digital breast tomosynthesis; mastectomy specimen; noise power spectra; out-of-plane blurring; super resolution.
Figures




References
-
- Paci E. Nass SJ, Henderson IC, L J (eds)., [Mammography and Beyond: Developing Technologies for Early Detection of Breast Cancer Washington, DC: National Academy Press, 2001. 316 pp] (2002).
-
- Dobbins JT and Godfrey DJ, “Digital x-ray tomosynthesis: Current state of the art and clinical potential,” Phys. Med. Biol 48(19) (2003). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
