Development of a visual detection method of porcine deltacoronavirus using loop-mediated isothermal amplification
- PMID: 39351303
- PMCID: PMC11439776
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1465923
Development of a visual detection method of porcine deltacoronavirus using loop-mediated isothermal amplification
Abstract
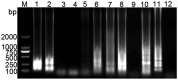
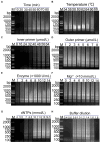
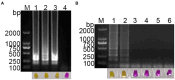
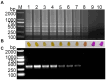
The emergence of porcine deltacoronavirus (PDCoV) presents a significant threat to both human and animal health due to its ability to cause highly contagious enteric diseases. This underscores the crucial need for timely and accurate diagnosis to facilitate effective epidemiological investigation and clinical management. This research aimed to establish a visual detection method based on reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) for PDCoV testing. In this study, six pairs of primers were designed according to the conserved sequences of PDCoV ORF1a/b genes. The primer sets and parameters that affect LAMP reaction were optimized. The visual RT-LAMP method was developed by incorporating methyl red into the optimized reaction system, it exclusively detected PDCoV without cross-reactivity with other viruses and the detection limits for PDCoV could reach 10 copies/μL. In comparison with RT-PCR for testing 132 clinical samples, the relative specificity and sensitivity of the visual RT-LAMP were found to be 99.2 and 100%, respectively, with a concordance rate of 99.2% and a kappa value of 0.959, indicating that the visual RT-LAMP is a reliable method for the application of PDCoV detection in clinical samples.
Keywords: deltacoronavirus; detection; loop-mediated isothermal amplification; porcine; visualization.
Copyright © 2024 Li, Cao, Yuan, Li, Zhou, Wang, Wang and Tian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chen X., Du C., Zhao Q., Zhao Q., Wan Y., He J., et al. (2023b). Rapid and visual identification of HIV-1 using reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification integrated with a gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow assay platform. Front. Microbiol. 14:1230533. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1230533, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dhama K., Karthik K., Chakraborty S., Tiwari R., Kapoor S., Kumar A., et al. (2014). Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA (LAMP): a new diagnostic tool lights the world of diagnosis of animal and human pathogens: a review. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 17, 151–166. doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2014.151.166, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

