Postural supporting cervical traction workstation to improve resting state brain activity in digital device users: EEG study
- PMID: 39351310
- PMCID: PMC11440563
- DOI: 10.1177/20552076241282244
Postural supporting cervical traction workstation to improve resting state brain activity in digital device users: EEG study
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to determine the effect of postural support workstation on inducing effective brain activity during rest.
Methods: Thirty-five healthy digital overusers were recruited as participants. We conducted two interventions of head weight support traction (ST) and conventional traction (CT) strength on all participants in random order. Participants' arousal levels and psychological comfort were assessed. In addition, changes in brain activity caused by traction were confirmed by measuring changes in resting state brain activity using an electroencephalogram (EEG).
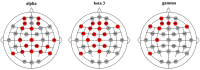
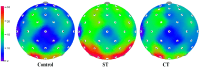
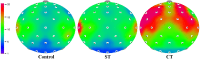
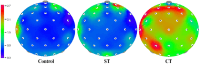
Results: Under the ST condition, psychological comfort improved while alert levels were maintained. In addition the resting brain activity of EEG was characterized by strong focused attention and relaxed activity, as evidenced by increased alpha waves throughout the brain. By contrast, in the CT condition, no significant improvement in comfort was observed. Furthermore, high-frequency brain activity, such as beta 3 and gamma waves, was observed across the entire brain regions.
Conclusion: In this study, the ST workstation was shown to effectively improve resting attention and psychological comfort in individuals who excessively use digital devices by inducing resting state alpha activity without stimulating high-frequency brain waves, while maintaining an upright posture with appropriate traction.
Keywords: Postural support workstations; cervical traction; comfort; ergonomics; focus attention; resting state attention.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

